Difference between revisions of "Seon Core configuration"
(→column defining connection type (ISDN, TCP/IP or TCP/IP TLS secured)) |
(→Fetch EERPs for ISDN partners, too?) |
||
| (261 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
*Odette | *Odette | ||
*Directories | *Directories | ||
| − | * | + | *Events |
*Daemon | *Daemon | ||
*Partner table | *Partner table | ||
| − | *GUI | + | *GUI |
| − | Each block is accessible with a link in the head of the configuration panel | + | Each block is accessible with a link in the head of the configuration panel. |
=== database method === | === database method === | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
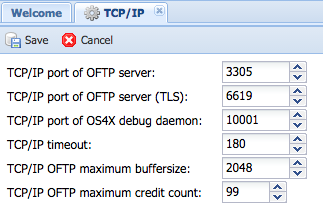
=== TCP/IP === | === TCP/IP === | ||
This block contains all basic TCP/IP parameters, such as port numbers, timeout values etc. | This block contains all basic TCP/IP parameters, such as port numbers, timeout values etc. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Config-tcpip.png]] | ||
==== TCP/IP port of OFTP server ==== | ==== TCP/IP port of OFTP server ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || tcp_port | ||
| + | |} | ||
This numeric value between 1 and 65535 describes the TCP/IP port the OFTP server is watching for incoming connections. The maximum of parallel incoming connections is limited by the operating system kernel and can be influenced by the kernel parameter "<code>SOMAXCONN</code>". | This numeric value between 1 and 65535 describes the TCP/IP port the OFTP server is watching for incoming connections. The maximum of parallel incoming connections is limited by the operating system kernel and can be influenced by the kernel parameter "<code>SOMAXCONN</code>". | ||
==== TCP/IP port of OFTP server (TLS) ==== | ==== TCP/IP port of OFTP server (TLS) ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || tcp_port_tls | ||
| + | |} | ||
This numeric value between 1 and 65535 describes the TCP/IP port the OFTP server is watching for incoming OFTP2 connections which are secured by TLS. The maximum of parallel incoming connections is limited by the operating system kernel and can be influenced by the kernel parameter "<code>SOMAXCONN</code>". This port must not be the same as the OFTP server port from above. | This numeric value between 1 and 65535 describes the TCP/IP port the OFTP server is watching for incoming OFTP2 connections which are secured by TLS. The maximum of parallel incoming connections is limited by the operating system kernel and can be influenced by the kernel parameter "<code>SOMAXCONN</code>". This port must not be the same as the OFTP server port from above. | ||
==== TCP/IP port of Seon debug daemon ==== | ==== TCP/IP port of Seon debug daemon ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || debugd_port | ||
| + | |} | ||
This numeric value between 1 and 65535 describes the TCP/IP port the OFTP server is watching for debug output. Every Seon program generates this output. The daemon collects this data and is able to dump this data in an encrypted file. This must not be the same as OFTP or OFTP 2 server ports. | This numeric value between 1 and 65535 describes the TCP/IP port the OFTP server is watching for debug output. Every Seon program generates this output. The daemon collects this data and is able to dump this data in an encrypted file. This must not be the same as OFTP or OFTP 2 server ports. | ||
==== TCP/IP timeout ==== | ==== TCP/IP timeout ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || tcp_timeout | ||
| + | |} | ||
This numeric value defines the maxmimum number of seconds between two TCP/IP packages to arrive. If this value is too low you might get network disconnects, setting this value very high means that a network disconnect will be discovered very late. | This numeric value defines the maxmimum number of seconds between two TCP/IP packages to arrive. If this value is too low you might get network disconnects, setting this value very high means that a network disconnect will be discovered very late. | ||
==== TCP/IP OFTP maximum buffersize ==== | ==== TCP/IP OFTP maximum buffersize ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftp_default_buffersize_tcpip | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | During the OFTP handshake, the maximum size of a data buffer will be commited. This value reflects the maximum size of such data buffers. The minimum value is 128, the maximum can be should not be over 65535 (because of TCP/IP packaging). The higher the value, the faster the data transfer rate will be (but it depends on the partner side). On unreliable connections, use the default value of 2048 bytes. | + | During the OFTP handshake, the maximum size of a data buffer will be commited. This value reflects the maximum size of such data buffers. The minimum value is 128, the maximum can be should not be over 65535 (because of TCP/IP packaging). The higher the value, the faster the data transfer rate will be (but it depends on the partner side). On unreliable connections, use the default value of 2048 bytes. For configurations with problemous partners like old Seeburger products, please use 800 bytes as buffersize. |
==== TCP/IP OFTP maximum credit count ==== | ==== TCP/IP OFTP maximum credit count ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftp_default_creditcount_tcpip | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | As the OFTP maximum buffersize, this value will be commited with the partner during a OFTP handshake. The number defines the amount of uncommited data buffers send to the receiver during file transfers. Increasing this value also increases the throughput. On unreliable connections you should use the default of 20. This is a different value than used for ISDN connections. | + | As the OFTP maximum buffersize, this value will be commited with the partner during a OFTP handshake. The number defines the amount of uncommited data buffers send to the receiver during file transfers. Increasing this value also increases the throughput. On unreliable connections you should use the default of 20. This is a different value than used for ISDN connections. For configurations with problemous partners like old Seeburger products, please use 20 as credit count. |
| − | + | ---- | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
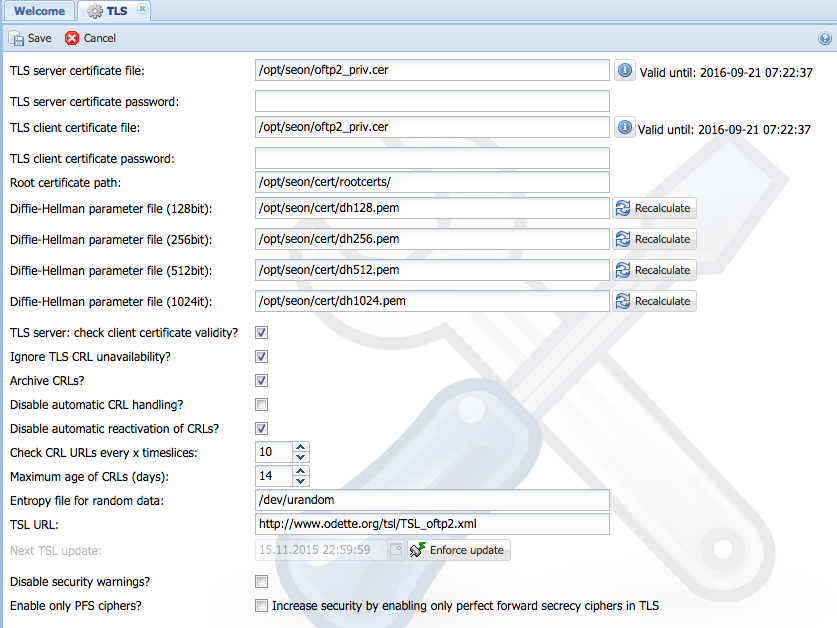
=== SSL/TLS parameters === | === SSL/TLS parameters === | ||
| Line 81: | Line 92: | ||
For securing TLS sessions over TCP/IP networks (such as internet), you need to give some information about your local certificates. These information don't have to be the same as for file based security. | For securing TLS sessions over TCP/IP networks (such as internet), you need to give some information about your local certificates. These information don't have to be the same as for file based security. | ||
| − | ==== | + | [[Image:Config-ssl.png]] |
| − | ''DB configuration name: tls_local_certificate & tls_server_cert_password | + | |
| + | ==== TLS server certificate file & TLS server certificate password ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || tls_local_certificate & tls_server_cert_password | ||
| + | |} | ||
Absolute path to the OFTP server certificate (in PEM format) for OFTP over TCP/IP (TLS secured). If the certificate is password-protected, you may enter it in the password field. | Absolute path to the OFTP server certificate (in PEM format) for OFTP over TCP/IP (TLS secured). If the certificate is password-protected, you may enter it in the password field. | ||
| − | ==== | + | ==== TLS client certificate file file & TLS client certificate password ==== |
| − | ''DB configuration name: tls_default_client_certificate & tls_client_cert_password | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || tls_default_client_certificate & tls_client_cert_password | ||
| + | |} | ||
Absolute path to the OFTP server certificate (in PEM format) for OFTP over TCP/IP (TLS secured). If the certificate is password-protected, you may enter it in the password field. | Absolute path to the OFTP server certificate (in PEM format) for OFTP over TCP/IP (TLS secured). If the certificate is password-protected, you may enter it in the password field. | ||
==== root certificate file & root certificate path ==== | ==== root certificate file & root certificate path ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: tls_root_certificate & tls_root_certpath' | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || tls_root_certificate & tls_root_certpath | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The root certificates are used to authentificate partners which have certificates of unknown signers. At least one of these fields must be filled (even if the root certificate path doesn't contain any root certificates). The certificates must be in PEM format. | ||
| − | + | These variables are (if set) available to processes started by Seon via the environment variables "<code>CA_FILE</code>" and "<code>CA_PATH</code>" (see also [[Seon Core environment variables]]). | |
==== Diffie-Hellman parameter files ==== | ==== Diffie-Hellman parameter files ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: dh128_file, dh256_file, dh512_file & dh1024_file | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || dh128_file, dh256_file, dh512_file & dh1024_file | ||
| + | |} | ||
These files (128bit, 256bit, 512bit and 1024bit) contain prime numbers, which are the basis for TLS encrypted connections. If the file is writable, or the file doesn't exist and the directory is writable, you can generate a new file from the web interface by using the link "Recalculate" or "Generate" in the web interface, which opens a new window which executes the command. Don't close this window until you can read the message "''You can | These files (128bit, 256bit, 512bit and 1024bit) contain prime numbers, which are the basis for TLS encrypted connections. If the file is writable, or the file doesn't exist and the directory is writable, you can generate a new file from the web interface by using the link "Recalculate" or "Generate" in the web interface, which opens a new window which executes the command. Don't close this window until you can read the message "''You can | ||
close this window now''"! | close this window now''"! | ||
| − | ==== | + | ==== TLS server: check client certificate validity ==== |
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || tls_server_check_client_cert | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | When this option is activated, all incoming TLS connections will be checked for a client certificate and a validity path for them. In case of self-signed certificates from the client, you have to add them manually (by requesting them from the partners) to your trusted certificate pool. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In case of client sessions, Seon will override a wrong purpose of the server certificate (such as "SSL client: no"). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Summarizing: | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you have this checkbox enabled (default): | ||
| + | *Seon's TLS server asks the remote side, if not already presented, during TLS handshake for a client certificate. | ||
| + | *This TLS client certificate is checked against the list of trusted certificates in order to verify a valid certificate chain for the certificate. | ||
| + | *If the certificate chain is trusted, all chain elements are checked against the actually installed certificate revocation lists ("CRLs"). | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you have this checkbox disabled (not the default, not recommended): | ||
| + | *None of the above checks is being executed. | ||
| + | *Every TLS client can connect to your server without any further client certificate check. | ||
| + | *Recommended only if: | ||
| + | **You have a firewall which applies partner defined rules, so you are sure who is connecting to your TLS server | ||
| + | **Have OFTP2 secure authentification enabled, in addition with the enabled "[[Seon_Core_configuration#enable_OFTP_message_checker|OFTP message checker]]" (in "Configuration" -> "Daemon") for protocol syntax validity verification (which lowers throughput and consumes higher server CPU). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Ignore TLS CRL unavailability? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || tls_ignore_crl_unavailable | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the above option "check client certificate validity" is activated, it is possible to deactivate the check of an existance of a CRL for all CA certificates which Seon doesn't have a CRL downloaded yet. This solves the problems with the following log entries the system log: | ||
| + | TLS error: no X509 certificate given in TLS handshake by remote partner | ||
| + | |||
| + | openSSL error: TLS network session failed, certificate problem: application verification failure | ||
| + | |||
| + | You must download a CRL for the CA of the certificate with the subject '...' | ||
| + | |||
| + | certificate verify error 3: unable to get certificate CRL: depth=0, subject: ... | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Archive CRLs? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || archive_crl | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | When activated, all overwritten CRLs will be archived before every update. When deleting CRLs, they will be archived, too. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Disable automatic CRL handling ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || disable_auto_crl | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Normally, the Seon send queue daemon scans all partner certificates for a new CRL URL and add them to the CRL list when not included. By activating this checkbox, you can disable this default behaviour. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Disable automatic reactivation of CRLs ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || crl_dont_automatic_reactivate | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If automatic CRL handling is not deactivated, Seon will enable all found disabled CRL entries found in certificates. If you don't want this behaviour, you can disable the reactivation by enabling this configuration option. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Check CRL URLs every x timeslices ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || autocrl_sendq_timeslices | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The send queue daemon can process every configured amount of timeslices (configured in the daemon section [[Seon_Core_configuration#time_slice_for_send_queue_daemon|here]]) all trusted certificates and their CRL distribution points. If any is not included in the revocation list yet, it will be added and handled. Cofiguration values above 512 and below 1 will be resetted to 10. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Maximum age of CRLs ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || maximum_crl_age | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | CRLs carry a date within them which defined when they become invalid. Seon takes care of such CRLs by downloading and updating the database values according to the new content. | |
| + | With this configuration parameter you make any CRL entry invalid (and therefore marked for automatic update) which has an older update date than these amount of days before. So, the locally downloaded version of the CRL becomes invalid and gets updated eventually even before the next CRL will be issued. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This feature is recommended by the OFTP2 working group. | ||
==== Entropy file for random data ==== | ==== Entropy file for random data ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: tls_entropy_file'' | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || tls_entropy_file | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | In order to use TLS, you have to specify a random data source. This is a kernel based character file (like "<code>/dev/urandom</code>" or "<code>/dev/random</code>"). If your operating system doesn't support such a random file (like AIX 5.1), you can generate such a file on your own (i.e. with the tool "ssh-rand-helper" from any openSSL installation). At least 256 bytes of random data must exist in this file. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== TSL URL ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || TSL_URL | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | This URL defines the position of a list administrated by Odette which contains a list of authorized certificate authorities. If the signed XML could be verified successfully, all contained certificate authorities are added automatically to Seon. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The default value is: | ||
| + | http://www.odette.org/TSL/TSL_OFTP2.XML | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Disable security warnings? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configTlsDisableSecurityWarnings | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | When enabled, Seon will never complain about insecure TLS cipher usage in connection logs (despite Seon SmartProxy logs, since the Seon SmartProxy doesn't support this insecurity "feature"). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Enable only PFS ciphers? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configTlsEnablePfs | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | When enabled, all incoming and outgoing TLS traffic will occure with a secure TLS cipher supporting a secure key exchange mechanism. A fallback to a less secure cipher is supported, but logged. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
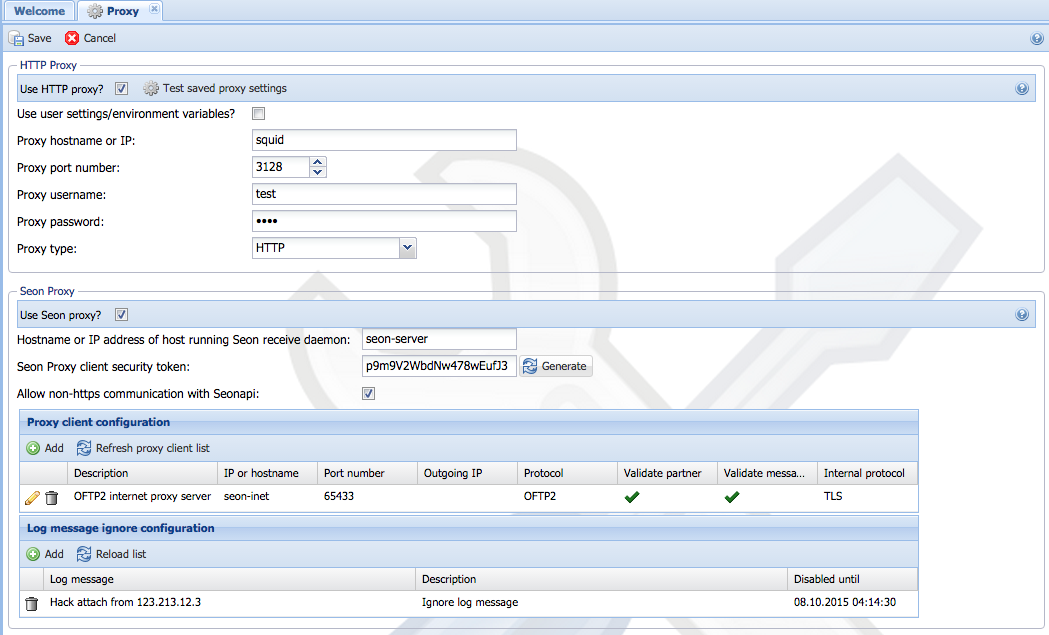
| + | === Proxy === | ||
| + | Seon offers for all HTTP and HTTPS transfer tasks proxy support. In order to use a defined proxy, several options are available. More details can be found [[Seon HTTP Proxy support|here]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Config-proxy.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Use HTTP proxy? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || proxy_enabled | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you want to use a proxy, enable this checkbox. If the checkbox is disabled, all proxy relevant environment variables (see [[Seon HTTP Proxy support]]) are cleared in all proxy using tools and binaries (and thus the forked processes by these binaries also don't have proxy environment variables defined). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Use user settings/environment variables? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || proxy_use_env | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If your used running Seon already has environmental variables defined for proper proxy support, you should enable this checkbox. Otherwise (if disabled), you have to configure the proxy in the parameter fields below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Proxy hostname or IP ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || proxy_host | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The resolvable hostname or IP address of the proxy server. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Proxy port number ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || proxy_port | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | The port number the proxy server is listening on. Only numbers are allowed here, from range 1-65535. Any other values will lead to misfunctions. Often used values are "8080" or "3128". | |
| + | |||
| + | ==== Proxy username ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || proxy_username | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If your proxy requires user authentification, enter a username here. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Proxy password ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || proxy_password | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If your proxy requires user authentification, enter the valid password for the above defined user. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Proxy type ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || proxy_type | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Different proxy types are supported, you should know which one fits your environment. Possible values are: | ||
| + | *SOCKS4 | ||
| + | *SOCKS5 | ||
| + | *HTTP | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Use Seon proxy? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || seon_proxy_enabled | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you want to use Seon proxy or Seon OFTP2 SmartProxy, enable this checkbox. Please refer to [[Seon Proxy|Seon Proxy]] and [[Seon SmartProxy|Seon OFTP2 SmartProxy]] for more detailled information. | ||
| + | ---- | ||
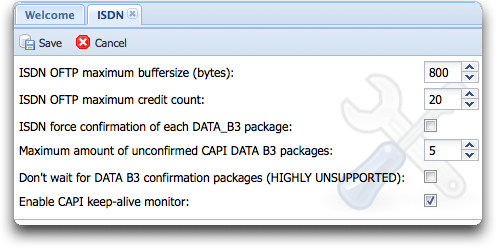
=== ISDN parameters === | === ISDN parameters === | ||
Basic ISDN parameters for OFTP connections have to be defined here. | Basic ISDN parameters for OFTP connections have to be defined here. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Config-isdn.png]] | ||
==== ISDN OFTP maximum buffersize ==== | ==== ISDN OFTP maximum buffersize ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftp_default_buffersize_isdn | ||
| + | |} | ||
As the TCP/IP maximum buffersize (as mentioned above), this numeric value reflects the | As the TCP/IP maximum buffersize (as mentioned above), this numeric value reflects the | ||
maximum size of a OFTP data buffer. It may result to problems if this is set to values | maximum size of a OFTP data buffer. It may result to problems if this is set to values | ||
higher than your ISDN controllers can use for maximum transfer size, which is limited by | higher than your ISDN controllers can use for maximum transfer size, which is limited by | ||
| − | CAPI2.0 to 4096 bytes. The minimum is 128 bytes. | + | CAPI2.0 to 4096 bytes. The minimum is 128 bytes. For configurations with problemous partners like old Seeburger products, please use 800 bytes as buffersize. |
==== ISDN OFTP maximum credit count ==== | ==== ISDN OFTP maximum credit count ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftp_default_creditcount_isdn | ||
| + | |} | ||
Same as the TCP/IP maximum credit count, this numeric value reflects the number of | Same as the TCP/IP maximum credit count, this numeric value reflects the number of | ||
| − | OFTP data exchange buffers before a little handshake will be done by the OFTP protocol. | + | OFTP data exchange buffers before a little handshake will be done by the OFTP protocol. For configurations with problemous partners like old Seeburger products, please use 20 as credit count. |
| + | |||
| + | ==== ISDN force confirmation of each DATA_B3 package ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || isdn_force_confirm_each_data_b3 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | In ISDN, all data is transfered in 128 byte blocks, so-called "DATA B3 packages". Each package has to be confirmed by the remote partner, so the ISDN subsystem can remove unneeded memory and do some cleanup. If the remote partner doesn't confirm all DATA B3 packages, you may force him do so by enabling this checkbox. The ISDN subsystem sets a special flag in the DATA B3 package so nearly every ISDN counter system should confirm the receipt of that package, even if it's not explicitely implemented. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== maximum amount of unconfirmed CAPI DATA B3 packages ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || max_capi_sliding_window_size | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Different ISDN systems support a different amount of unconfirmed DATA B3 packages (see above). The normal CAPI standard of seven (7) unconfirmed DATA packages should never be reached, so you should be one or two packages lower than that limit in order to achieve the maximum of transport speed. Special CAPI ISDN implementations support more that the standard of seven packages, i.e. Bintec Bricks (they support up to 15). It doesn't make any sense to use that amount of unconfirmed data buffers, it doesn't speed up the transfer any more. If you receive CAPI timeouts, you should lower this amount of packages. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Don't wait for DATA B3 confirmation packages ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || isdn_dont_wait_for_data_b3_conf | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If your ISDN system supports an extreme data throughput and nearly unlimited amount of unconfirmed DATA B3 packages lying around, you may ignore and don't wait for DATA B3 confirmation packages by enabling this '''highly unsupported''' feature. If you encounter line disconnects, disable this feature! | ||
| + | |||
| + | <u>Background:</u> In "''normal''" ISDN wildlife, each DATA B3 indication package indicates that other DATA B3 confirmation packages (up to this point of protocol transfer time) have been received. TIf you transfer very little files, it may be annoying waiting for each single data confirm package, you could send the file "as is" and wait for the OFTP protocol confirmation instead of waiting for the ISDN subsystem to acknowledge each single small piece of data sent. In some cases it's helpful, in most it's not! '''Just keep the setting disabled as long as you know exactly what you are doing!''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== enable CAPI keep-alive monitor ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || capi_check_alive_monitor | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | In order to use a Brick R4x00 or above, you have to enable this feature. Also, if you don't want to watch for Seon after a reboot of the Brick device, enable this feature. | ||
| + | Activating this feature, Seon checks every defined controller every 60 seconds for availability. If a controller is inaccessible, it tries the connectivity again after 60 seconds. | ||
| + | --- | ||
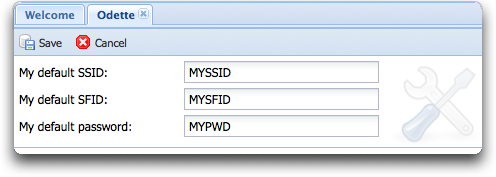
=== Odette parameters === | === Odette parameters === | ||
Default OFTP parameters for authentifications are configurable here. If no special columns are defined in the partner table below, these values will be used. | Default OFTP parameters for authentifications are configurable here. If no special columns are defined in the partner table below, these values will be used. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Config-odette.png]] | ||
==== my default SSID, my default SFID, my default OFTP password, change every partner entry ==== | ==== my default SSID, my default SFID, my default OFTP password, change every partner entry ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: default_ssid, default_sfid & default_password | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || default_ssid, default_sfid & default_password | ||
| + | |} | ||
These elements are only used for the web interface for creating new partners or for | These elements are only used for the web interface for creating new partners or for | ||
| Line 139: | Line 397: | ||
get the new values for SSID, SFID and password on your side. If you don't configure | get the new values for SSID, SFID and password on your side. If you don't configure | ||
columns in the partner table configuration below, these values are used for OFTP | columns in the partner table configuration below, these values are used for OFTP | ||
| − | authentification. | + | authentification. |
| + | ---- | ||
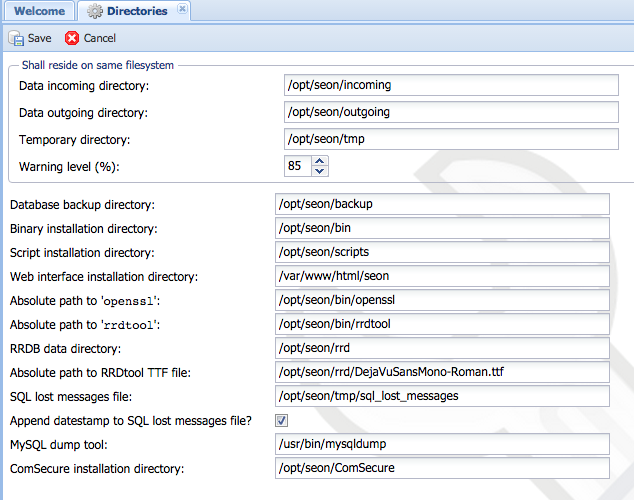
=== Directories === | === Directories === | ||
In order to let Seon know where to find directories and files, these values have to be defined. | In order to let Seon know where to find directories and files, these values have to be defined. | ||
| + | [[Image:Config-directories.png]] | ||
==== data incoming directory ==== | ==== data incoming directory ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || incoming_directory | ||
| + | |} | ||
After successful file transfers (receiving), this directory defines where the incoming files will be stored. This directory must be on the same filesystem as the temporary directory (see below), otherwise you will get an error message in syslog (if enabled) that moving incoming files cannot be done. | After successful file transfers (receiving), this directory defines where the incoming files will be stored. This directory must be on the same filesystem as the temporary directory (see below), otherwise you will get an error message in syslog (if enabled) that moving incoming files cannot be done. | ||
| Line 151: | Line 414: | ||
==== data outgoing directory ==== | ==== data outgoing directory ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || outgoing_directory | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | This directory will be used by Seon Webaccess (which is part of Seon Enterprise) for outgoing jobs when initiating a send job. The plugins | |
| + | [[Seon plugin seonplugin_filemove|seonplugin_filemove]] and [[Seon plugin seonplugin_filecopy|seonplugin_filecopy]] can refer to this directory by a configuration value. | ||
==== temporary directory ==== | ==== temporary directory ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || tmp_directory | ||
| + | |} | ||
During incoming file transfers, the file fragments will be stored in this directory. Keep in mind (as mentioned above) to set this directory to the same filesystem as the [[Seon Core configuration#data incoming directory|incoming directory]]. The filesystem must be dimensioned big enough to store a file with at most the maximum | During incoming file transfers, the file fragments will be stored in this directory. Keep in mind (as mentioned above) to set this directory to the same filesystem as the [[Seon Core configuration#data incoming directory|incoming directory]]. The filesystem must be dimensioned big enough to store a file with at most the maximum | ||
| Line 162: | Line 432: | ||
==== database backup directory ==== | ==== database backup directory ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || backup_directory | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | If you want to use the Seon backup | + | If you want to use the Seon backup mechanism, you need to define a directory where the SQL dump files will be stored. This directory is needed for the scripts "seonbackup" and "seonrestore". |
==== binary installation directory ==== | ==== binary installation directory ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || bin_directory | ||
| + | |} | ||
This directory points to your binary installation of Seon. It also contains the license key, so if you receive a license error, first check the existence of this directory and the file "license.key" in it. This entry is also used for the web interface to start the daemons. | This directory points to your binary installation of Seon. It also contains the license key, so if you receive a license error, first check the existence of this directory and the file "license.key" in it. This entry is also used for the web interface to start the daemons. | ||
==== script installation directory ==== | ==== script installation directory ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || script_directory | ||
| + | |} | ||
This directory points to your script installation of Seon. It contains helpful scripts, such as database backup and restore scripts and maybe other useful tools. The Seon web interface uses this definition. | This directory points to your script installation of Seon. It contains helpful scripts, such as database backup and restore scripts and maybe other useful tools. The Seon web interface uses this definition. | ||
==== absolute path to 'openssl' ==== | ==== absolute path to 'openssl' ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || tcp_timeout | ||
| + | |} | ||
''DB configuration name: openssl_binary_path'' | ''DB configuration name: openssl_binary_path'' | ||
| − | Seon uses openSSL as basis for all OFTP 2 file security functions. The configured binary must exist and be executable for the user running Seon processes. | + | Seon uses openSSL as basis for all OFTP 2 file security functions. The configured binary must exist and be executable for the user running Seon processes. |
| + | The used openSSL binary must be of version 0.9.9dev, 1.0.0 or higher to fulfill the functionality for OFTP2. | ||
==== absolute path to 'rrdtool' ==== | ==== absolute path to 'rrdtool' ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || rrdtool_binary_path | ||
| + | |} | ||
In order to use statistics, you have to define the path to „rrdtool“, the Round Robin database tool by Tobias Oetiker. The standard Seon distribution contains a pre-compiled version which works within Seon. If the file configured isn't executable, statistics are disabled. The program is used to create databases within Seon binaries, push data in it and to display the results as graphical output in the web interface. | In order to use statistics, you have to define the path to „rrdtool“, the Round Robin database tool by Tobias Oetiker. The standard Seon distribution contains a pre-compiled version which works within Seon. If the file configured isn't executable, statistics are disabled. The program is used to create databases within Seon binaries, push data in it and to display the results as graphical output in the web interface. | ||
| Line 188: | Line 475: | ||
==== RRDB data path ==== | ==== RRDB data path ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || rrdb_datapath | ||
| + | |} | ||
In this path, Seon creates, stores, modifies and searches the files for statistics. The directory must be writable by the user running Seon. If the path isn't writable or doesn't exists, statistics are disabled. For each partner, a file is generated for incoming transfer and for outgoing. The total consumption on the filessystem is about 315kB per partner. | In this path, Seon creates, stores, modifies and searches the files for statistics. The directory must be writable by the user running Seon. If the path isn't writable or doesn't exists, statistics are disabled. For each partner, a file is generated for incoming transfer and for outgoing. The total consumption on the filessystem is about 315kB per partner. | ||
==== absolute path to RRDtool TTF file ==== | ==== absolute path to RRDtool TTF file ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || rrdtool_font_path | ||
| + | |} | ||
The statistical overview needs a font file (as Truetype font). Without this font file, you won't get any textual information in the statistic graphs. | The statistical overview needs a font file (as Truetype font). Without this font file, you won't get any textual information in the statistic graphs. | ||
==== SQL lost messages file ==== | ==== SQL lost messages file ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || sql_lost_messages_file | ||
| + | |} | ||
If the configured MySQL server isn't reachable at any time, the SQL statements which are being sent to the MySQL server are logged into this file. If the file doesn't exists it will be created, so the directory must be writable for the user running Seon. The file itself (if it exists) must also be writable by the user running Seon. | If the configured MySQL server isn't reachable at any time, the SQL statements which are being sent to the MySQL server are logged into this file. If the file doesn't exists it will be created, so the directory must be writable for the user running Seon. The file itself (if it exists) must also be writable by the user running Seon. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Append datestamp to SQL lost messages file? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || sql_lost_messages_file_append_timestamp | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If enabled, in case of database inaccessibility, all SQL statements which could not be executed will be logged in the above configured "SQL lost message file", which gets a datestamp appendix to the filename. This datestamp consists of the following: | ||
| + | *a single dot ("<code>.</code>") | ||
| + | *year with 4 digits (like "<code>2009</code>") | ||
| + | *month with 2 digits (like "<code>03</code>") | ||
| + | *day with 2 digits (like "<code>27</code>") | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example with a lost message fole configured to "<code>/opt/seon/tmp/sql_lost_messages</code>": | ||
| + | /opt/seon/tmp/sql_lost_messages.20090307 | ||
| + | |||
| + | /opt/seon/tmp/sql_lost_messages.20090130 | ||
==== MySQL dump tool ==== | ==== MySQL dump tool ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || mysqldump | ||
| + | |} | ||
As a useful tool from each MySQL distribution, the tool "<code>mysqldump</code>" is used in the Seon backup script for doing its job. | As a useful tool from each MySQL distribution, the tool "<code>mysqldump</code>" is used in the Seon backup script for doing its job. | ||
| − | === | + | ==== send test file ==== |
| + | If configured correctly, Seon displays a link [[Image:System-software-update.gif]] for test purposes for a partner. A given file can be sent with a given virtual filename to that partner for checking the OFTP connection. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
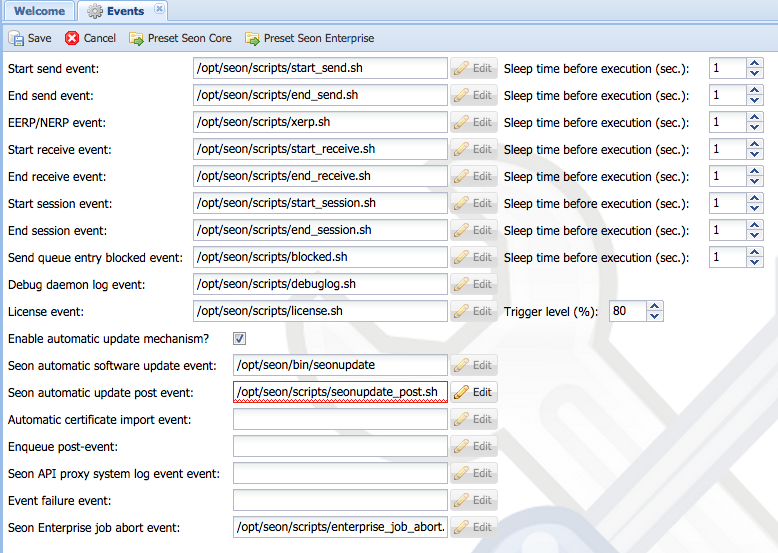
| + | === Events === | ||
| + | [[Image:Config-events.png]] | ||
| + | |||
First some words about the global behaviour of scripts: | First some words about the global behaviour of scripts: | ||
==== event script usage ==== | ==== event script usage ==== | ||
Every time the configuration of Seon is checked by a binary (which is at start time or when processing the signal 1 - SIGHUP), the event script configuration is checked. If a script is non-existant and/or the execute permissions don't allow the execution of a configured script, it won't get executed. No warning will be printed out or logged somewhere. | Every time the configuration of Seon is checked by a binary (which is at start time or when processing the signal 1 - SIGHUP), the event script configuration is checked. If a script is non-existant and/or the execute permissions don't allow the execution of a configured script, it won't get executed. No warning will be printed out or logged somewhere. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Presets exist (which are dynamically calculated with the last saved values for the scripts and binary directory configured [[Seon_Core_configuration#binary_installation_directory|here]]). These presets could be used for easy resetting the script configuration to either Seon Enterprise (Lite) and/or Seon 2 Core. | ||
==== event script sleep time ==== | ==== event script sleep time ==== | ||
| Line 217: | Line 544: | ||
==== start send script ==== | ==== start send script ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: start_send_script & sleep_start_send_script | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || start_send_script & sleep_start_send_script | ||
| + | |} | ||
If a file is getting sent, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters. | If a file is getting sent, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters. | ||
==== end send script ==== | ==== end send script ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: end_send_script & sleep_end_send_script | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || end_send_script & sleep_end_send_script | ||
| + | |} | ||
If a file has finished (successfully or not) sending, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters. | If a file has finished (successfully or not) sending, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters. | ||
==== xERP script ==== | ==== xERP script ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: xerp_script & sleep_xerp_script | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || xerp_script & sleep_xerp_script | ||
| + | |} | ||
If an EERP or NERP (OFTP 2 only) message is received, this script will be started. Seon tries to find a send queue entry which conforms to the given parameters in order to set the values for comment, absolute path etc. If no send queue entry can be found that matches the given parameters in the EERP or NERP message, the script won't be executed. This script receives the same parameters as the [[Seon Core configuration#end send script|end send script]] script. | If an EERP or NERP (OFTP 2 only) message is received, this script will be started. Seon tries to find a send queue entry which conforms to the given parameters in order to set the values for comment, absolute path etc. If no send queue entry can be found that matches the given parameters in the EERP or NERP message, the script won't be executed. This script receives the same parameters as the [[Seon Core configuration#end send script|end send script]] script. | ||
==== start receive script ==== | ==== start receive script ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: start_receive_script & sleep_start_receive_script | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || start_receive_script & sleep_start_receive_script | ||
| + | |} | ||
If a file is getting received, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters. | If a file is getting received, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters. | ||
==== end receive script ==== | ==== end receive script ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: end_receive_script & sleep_end_receive_script | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || end_receive_script & sleep_end_receive_script | ||
| + | |} | ||
If a file has finished (successfully or not) receiving, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters. | If a file has finished (successfully or not) receiving, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters. | ||
==== start session script ==== | ==== start session script ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: start_session_script & sleep_start_session_script | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || start_session_script & sleep_start_session_script | ||
| + | |} | ||
After a positive OFTP handshake, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters. | After a positive OFTP handshake, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters. | ||
==== end session script ==== | ==== end session script ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: end_session_script & sleep_end_session_script | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || end_session_script & sleep_end_session_script | ||
| + | |} | ||
After a positive OFTP session, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters. | After a positive OFTP session, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters. | ||
==== send queue entry blocked script ==== | ==== send queue entry blocked script ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: blocked_script & sleep_blocked_script | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || blocked_script & sleep_blocked_script | ||
| + | |} | ||
If a send queue entry gets blocked (i.e. wrong authentification, unsupported virtual filename at the remote site, connection problems), this scripts will be started. If more than one entry for a partner gets blocked, each send queue entry will start its own blocked script. | If a send queue entry gets blocked (i.e. wrong authentification, unsupported virtual filename at the remote site, connection problems), this scripts will be started. If more than one entry for a partner gets blocked, each send queue entry will start its own blocked script. | ||
==== debug daemon log script ==== | ==== debug daemon log script ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || seondebugd_log_script | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | After a debug log has been written, this script will be started. This can be the case when asking for a debug log interactively (or with starting the appropriate program manually) or, if configured, when automatically created debug logs are written. | + | After a debug log has been written, [[Seon_Core_event_scripts#debug_daemon_log_script|this script will be started]]. This can be the case when asking for a debug log interactively (or with starting the appropriate program manually) or, if configured, when automatically created debug logs are written. |
==== license script & trigger level ==== | ==== license script & trigger level ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: license_script & license_script_hwm | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || license_script & license_script_hwm | ||
| + | |} | ||
This script will be started after a configurable trigger level (in percent) is exceeded. Its main porpuse is to inform a responsible person that a new license should be obtained or other actions should be taken. | This script will be started after a configurable trigger level (in percent) is exceeded. Its main porpuse is to inform a responsible person that a new license should be obtained or other actions should be taken. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Enable automatic update mechanism & Seon automatic software update event ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || run_updates_automatically & seonupdate_script | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the value of ''run_updates_automatically'' is non-zero (if the checkbox is enabled), the automatic update script is started with the received file with the reserved virtual filename "<code>SEON-UPDATE</code>". This is normally a program of the Seon distribution in order to update the installation via signed files. This program changes its user context to the configured user (see: [[Seon_Core_configuration#run_Seon_update_program_as_user|run Seon update program as user]]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Seon automatic update post event ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configEventUpdatePost | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | After a software update has been executed via the program "[[Seon_Core_binaries#seonupdate|seonupdate]]", the configurable post event can be started, i.e. for cleanup reasons or informing system management hierachies. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== enqueue post-script ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || enqueue_post_script | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | This script which will be executed after a successful enqueueing process. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Seon API proxy system log event script ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || seonapi_proxy_systemlog_script | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | This script which will be executed after a critical situation of the Seon Proxy will be logged in the Seon system log. | ||
| + | ---- | ||
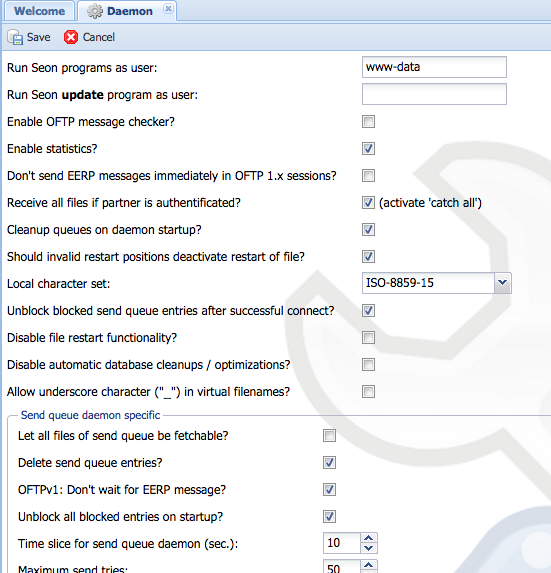
=== Daemon parameters === | === Daemon parameters === | ||
The behaviour of all binaries and Seon programs can be influenced here. | The behaviour of all binaries and Seon programs can be influenced here. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Config-daemon.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== run Seon programs as user ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || running_as_user | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | When starting as user "<code>root</code>", all Seon binaries will try to switch to this configured user, if available on the running system. Subsequent calls of scripts and other programs are also done in the context of this user. This is extremely useful for runlevel scripts. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Double-check that this user exists in the system running Seon, that is has a home directory which is accessible and writable and that this user has a shell configured which is runnable!''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== run Seon update program as user ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || running_update_as_user | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If enabled below, automatic software update are being run using this specific username. If changing to the context of this given user fails, the whole update procedure fails. If no username is configured, superuser "<code>root</code>" is used. | ||
==== time slice for send queue daemon ==== | ==== time slice for send queue daemon ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || seonsqd_sleep_time | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | The send queue daemon | + | The send queue daemon „seonsqd“ waits this amount of seconds before looking at the send queue table and react as needed (send one more entry, wait more time etc.). |
==== time slice for receive daemon ==== | ==== time slice for receive daemon ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || seonrd_sleep_time | ||
| + | |} | ||
The receiving daemon „seonrd2“ waits this amount of seconds before looking at the configuration table and react as needed (wait more time or stop itself). | The receiving daemon „seonrd2“ waits this amount of seconds before looking at the configuration table and react as needed (wait more time or stop itself). | ||
==== delete send queue entries ==== | ==== delete send queue entries ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: delete_after_transfer'' | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || delete_after_transfer | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | This checkbox defines if the send queue table entries should be deleted (not the files itself, only the entry!) after a successful send. (If you need to delete the file itself, you should use the [[Seon Core configuration#end_send_script|end send script]], which gets the absolute filename as a parameter). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | If this option is enabled, it automatically disabled the following option "Cleanup of sent send queue entries". | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Cleanup of sent send queue entries ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configSendqueueCleanup | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If enabled, the send queue daemon cleans up the send queue for all entries with a given age automatically (based on the timestamp of "last change"). Optionally, an event "[[OS4X_Core_event_scripts#Send_queue_cleanup_event|Send queue cleanup event]]" will be executed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Age of send queue entries for cleanup (days) ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configSendqueueCleanupDays | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Send queue entries in status "successfully sent" with the last change date older than this amount of days will be taken into account for automatic cleanup. | ||
| − | + | ===== Delete file, if available ===== | |
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configSendqueueCleanupDeleteFile | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If this option is enabled, the automatic cleanup mechanism will delete the referenced file on the filesystem. If file deletion will take place, a log message will look like: | ||
| + | Deleted send queue entry '<virt. filename>' and file '<abs. filename>' | ||
| + | |||
| + | If this option is disabled or the referenced file doesn't exist, the log message says: | ||
| + | Deleted send queue entry '<virt. filename>' | ||
==== let all files of send queue be fetchable ==== | ==== let all files of send queue be fetchable ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || fetch_all_from_remote | ||
| + | |} | ||
Since polling is supported from remote systems, you can define files to be pollable. If you enable this checkbox, all files in your send queue which are in state of "new in queue" and "ready for remote fetch" will be sent in an OFTP session to the partner (otherwise, only entries "ready for remote fetch" are fetchable). | Since polling is supported from remote systems, you can define files to be pollable. If you enable this checkbox, all files in your send queue which are in state of "new in queue" and "ready for remote fetch" will be sent in an OFTP session to the partner (otherwise, only entries "ready for remote fetch" are fetchable). | ||
==== overwrite existing incoming files ==== | ==== overwrite existing incoming files ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || seonrd_overwrite | ||
| + | |} | ||
If the incoming file exists in the "[[Seon Core configuration#data incoming directory|incoming directory]]", you can define to overwrite it. Otherwise, the partner will receive an error message saying that the local file already exists. (this might be useful for partners who don't like to reiceive an EEPR [end-to-end- response] message right after a successful filetransfer). | If the incoming file exists in the "[[Seon Core configuration#data incoming directory|incoming directory]]", you can define to overwrite it. Otherwise, the partner will receive an error message saying that the local file already exists. (this might be useful for partners who don't like to reiceive an EEPR [end-to-end- response] message right after a successful filetransfer). | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==== default maximum send tries for send queue daemon ==== | ==== default maximum send tries for send queue daemon ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || seonsqd_max_tries | ||
| + | |} | ||
The send queue daemon "seonsqd2" will try to send one or all entries this amount of times. After this amount of unsuccessful tries, one or all send queue entries for that partner will be blocked (which will also get logged into the send log). All entries for a partner get blocked, if a connection problem occurs (i.e. invalid SSID/SFID or password, no physical connection to partner, wrong ISDN number or TCP/IP address etc.). One entry will be blocked if the partner doesn't accept this file. The other files are not affected by that error (i.e. wrong virtual filename, wrong alternative SFID of originator or destination). | The send queue daemon "seonsqd2" will try to send one or all entries this amount of times. After this amount of unsuccessful tries, one or all send queue entries for that partner will be blocked (which will also get logged into the send log). All entries for a partner get blocked, if a connection problem occurs (i.e. invalid SSID/SFID or password, no physical connection to partner, wrong ISDN number or TCP/IP address etc.). One entry will be blocked if the partner doesn't accept this file. The other files are not affected by that error (i.e. wrong virtual filename, wrong alternative SFID of originator or destination). | ||
==== additional sleeping time for send queue daemon & additional sleeping time factor for send queue daemon ==== | ==== additional sleeping time for send queue daemon & additional sleeping time factor for send queue daemon ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: seonsqd_add_time & seonsqd_add_time_factor | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || seonsqd_add_time & seonsqd_add_time_factor | ||
| + | |} | ||
You can influence the time the send queue daemon „seonsqd2“ will sleep before it tries | You can influence the time the send queue daemon „seonsqd2“ will sleep before it tries | ||
| Line 318: | Line 769: | ||
==== progress bar refresh time ==== | ==== progress bar refresh time ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || progressbar_refresh | ||
| + | |} | ||
Seon will update all file transfer progress information after this value (in seconds). Because it is database driven, some MySQL server will crash if you have too many connects to a database in a very short time (which could occur if you transfer very little files with a combination of a small exchange buffer size). If you experience problems with your database server, try increasing this value. | Seon will update all file transfer progress information after this value (in seconds). Because it is database driven, some MySQL server will crash if you have too many connects to a database in a very short time (which could occur if you transfer very little files with a combination of a small exchange buffer size). If you experience problems with your database server, try increasing this value. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
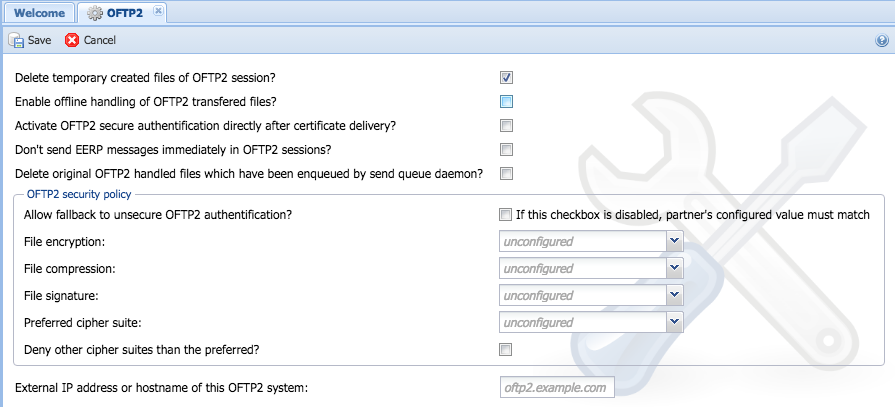
==== allow unsecure OFTP 2 authentification ==== | ==== allow unsecure OFTP 2 authentification ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftpv2_allow_unsecure_auth | ||
| + | |} | ||
If an OFTP 2 partner is requested to use OFTP 2 authentification but he doesn't support this feature, you may allow to authentificate this partner with the OFTP 1 methods by enabling this checkbox. If you insist to use OFTP 2 authentification, disable the checkbox, so the partner will receive an error message that OFTP 2 secure authentification is needed. | If an OFTP 2 partner is requested to use OFTP 2 authentification but he doesn't support this feature, you may allow to authentificate this partner with the OFTP 1 methods by enabling this checkbox. If you insist to use OFTP 2 authentification, disable the checkbox, so the partner will receive an error message that OFTP 2 secure authentification is needed. | ||
==== delete temporary created files of OFTP 2 session ==== | ==== delete temporary created files of OFTP 2 session ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftpv2_delete_temp_created_files | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | Seon creates temporary files by enqueueing files to the send queue or by directly sending a file to an OFTP 2 partner (if the partner is configured to use signing, compression and/or encryption). These temporary files can be deleted by Seon automatically, but you may also want to keep them for later archiving | + | Seon creates temporary files by enqueueing files to the send queue or by directly sending a file to an OFTP 2 partner (if the partner is configured to use signing, compression and/or encryption). These temporary files can be deleted by Seon automatically, but you may also want to keep them for later archiving. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==== local character set ==== | ==== local character set ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftpv2_original_charset | ||
| + | |} | ||
OFTP 2 supports UTF-8 formatted information and error messages within the protocol and also extended virtual filenames (up to 999 bytes of UTF-8 formatted text). To translate the UTF-8 text into your local character set and to translate command line interaction from your local character set to UTF-8, you have to define your local character set here. If your local character set isn't listed here, you can define it in the database (table: "seon_configuration") manually by entering the character set descriptor in the line where „name“ is "oftpv2_original_charset". All character sets which are supported by "iconv" are supported by Seon. You get a list of supported character sets on the command line with the program: | OFTP 2 supports UTF-8 formatted information and error messages within the protocol and also extended virtual filenames (up to 999 bytes of UTF-8 formatted text). To translate the UTF-8 text into your local character set and to translate command line interaction from your local character set to UTF-8, you have to define your local character set here. If your local character set isn't listed here, you can define it in the database (table: "seon_configuration") manually by entering the character set descriptor in the line where „name“ is "oftpv2_original_charset". All character sets which are supported by "iconv" are supported by Seon. You get a list of supported character sets on the command line with the program: | ||
iconv -l | iconv -l | ||
| − | if installed. | + | if installed. |
| + | |||
| + | ==== Unblock blocked send queue entries after successful connect? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || unblock_blocked_sendqueue_entries_after_poll | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If enabled, this options lets the Seon poll binary and receive daemon unblock blocked send queue entries after a incoming or outgoing connection to this partner has been successfully established. | ||
| − | ==== | + | ==== Disable file restart functionality? ==== |
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configDaemonDisableFilerestart | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | If enabled, Seon doesn't offer file restart functionality (which is offered by default if the communication partner supports it). In this case, the partner is told not to support file resuming, so aborted file transfers will restart in future sessions from the beginning of the file. | |
| − | ==== | + | ==== Disable automatic database cleanups / optimizations? ==== |
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configDaemonDisableMysqlOptimizeTables | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | Seon cleans up database tables after a successful delete operation (in MySQL via "<code>OPTIMIZE TABLE</code>", in SQLite via "<code>VACUUM</code>" command). Enabling this configuration option disables the automatic cleanup of tables. '''Warning:''' could make your database grow in size if you don't clean up on your own! | |
==== enable OFTP message checker ==== | ==== enable OFTP message checker ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftp_message_checker | ||
| + | |} | ||
To secure your server, an OFTP message checker examines each transfered package for validity. This suppresses protocol attacks from remote and helps to avoid NULL pointer exceptions and other well-known attacks. | To secure your server, an OFTP message checker examines each transfered package for validity. This suppresses protocol attacks from remote and helps to avoid NULL pointer exceptions and other well-known attacks. | ||
==== send queue entry status after abort ==== | ==== send queue entry status after abort ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || sendq_entry_status_after_abort | ||
| + | |} | ||
You can define the status of a send queue entry after manual abort here. It may be useful to avoid a race between an administrator and the send queue daemon if he aborts the file transfer but the send queue daemon grabs it afterwards because the time slice has taken account. Valid options are "new in queue", "successfully sent", "blocked" and "ready for remote fetch". | You can define the status of a send queue entry after manual abort here. It may be useful to avoid a race between an administrator and the send queue daemon if he aborts the file transfer but the send queue daemon grabs it afterwards because the time slice has taken account. Valid options are "new in queue", "successfully sent", "blocked" and "ready for remote fetch". | ||
| − | ==== enable | + | ==== enable statistics & RRDtools refresh time ==== |
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || enable_statistics & rrd_refresh | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | As configured above with the RRDtool paths and directories, you have the possibility to activate or deactivate the scripting functionality here. The statistics contain the average transfer speed of a partner (incoming and outgoing as separate databases). If any of the above configured RRDtool path or binary is unavailable, scripting is disabled, even if you enable it here. The refresh time is the time is seconds when statistical data is transfered into the Round Robin database. This time period depends also on the database configuration of the RRDB and is closely dependant from the creation process which is intergrated into Seon (if an RRDB file doesn't exist). The default of 10 seconds should not be changed! | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''NEW:''' If statistics are enabled, a seperate logging table will be filled with information how many files have been transfered (in the ways "sent" and "received" with or without success. This amount of transfered filed is being displayed in the partner list and the partner "edit" details. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Append timestamp to received file ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || rec_append_timestamp_to_filename | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Some partners may send you files with the same virtual filename, but different timestamps. In order to receive these files properly, an appendix is added to the filename containing the announced timestamp of the file. This also helps to receive the same file from different partners at the same time. | ||
| + | Beware: the timestamp syntax has changed from OFTP 1 to OFTP 2! | ||
| + | |||
| + | The appendix of the filename is as follows: | ||
| + | *OFTP 1.0 - OFTP 1.3: "<code><datestamp><timestamp>0000</code>", i.e. "<code>200903171423590000</code>" | ||
| + | *OFTP 1.4 and OFTP2: "<code><datestamp><timestamp><counter></code>", i.e. "<code>200903171423590523</code>" | ||
| − | + | The main difference between both names is that the "counter" field in older OFTP sessions will be emulated via "<code>0000</code>". | |
| − | ==== | + | ==== Append destination SFID to received file ==== |
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configDaemonAppendSFIDRec | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | If enabled, the received file will contain the destination SFID attached with a dot ("<code>.</code>") in front of the SFID to the filename. This influences both the temporary and absolute filename after transfer. | |
| − | ==== | + | ==== Append PID of receive process to received file ==== |
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configDaemonAppendPIDRec | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | If enabled, the received file will contain the process ID (so-called "PID") attached with a dot ("<code>.</code>") in front of the PID to the filename. This influences both the temporary and absolute filename after transfer. | |
| − | |||
==== OFTPv1: Don't wait for EERP message ==== | ==== OFTPv1: Don't wait for EERP message ==== | ||
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftpv1_dont_wait_for_eerp | ||
| + | |} | ||
The normal behaviour of a send queue item is as follows: | The normal behaviour of a send queue item is as follows: | ||
| Line 396: | Line 897: | ||
If an partner doesn't send an EERP message, the send queue entry will exist forever. In order to avoid this, the send queue entry may get the status „successfully sent“ after successful send by enabling this checkbox (and may be deleted if the above checkbox „delete send queue entries“ is enabled). Beware: the xERP scripts won't be executed any more because no send queue entry will be found matching the parameters given in any EERP or NERP message. '''This feature just affects OFTP v1 partners, not OFTP 2!''' | If an partner doesn't send an EERP message, the send queue entry will exist forever. In order to avoid this, the send queue entry may get the status „successfully sent“ after successful send by enabling this checkbox (and may be deleted if the above checkbox „delete send queue entries“ is enabled). Beware: the xERP scripts won't be executed any more because no send queue entry will be found matching the parameters given in any EERP or NERP message. '''This feature just affects OFTP v1 partners, not OFTP 2!''' | ||
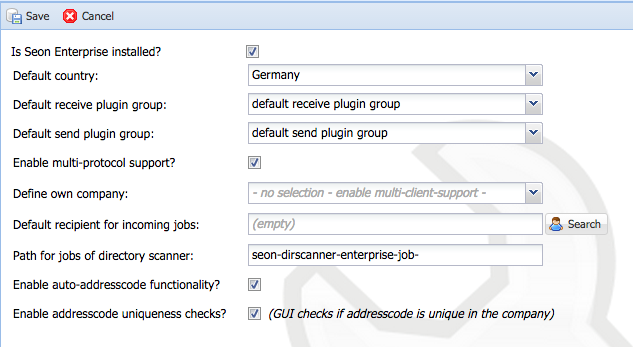
| − | ==== is Seon Enterprise installed? ==== | + | ==== Enable automatic update mechanism? ==== |
| − | ''DB configuration name: | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || run_updates_automatically | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Activating this feature enables the usage of automatic software and lowers the administrative tasks to keep the software up-to-date. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Send queue daemon partner organizing mechanism ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || sqd_partner_organizing | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you want to configure a massive parallel installation to be handled by the send queue daemon without shared memory segments for information handling which partner has how many lines online, you may want to switch this configuration value to "database values". The default of "shared memory segments" works perfectly for single instances of Seon and should be set only this way. '''CAVEAT: when using database values only for parallel channel information on send queue partners, there exists a timeframe when the information is invalid (this is when the send queue daemon forks a new process up to the database update command execution). During this little amount of time, more parallel processes may exist than configured for this partner.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== take ALL server IDs into account ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || sqd_db_partner_organizing_all | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the above configuration of "Send queue daemon partner organizing mechanism" is set to "database values", then only this server ID could be inspected or ALL used servers can be inspected for parallel channels. '''Enabling this checkbox is the recommended value for this configuration!''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== also take receive queue into account ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || sqd_partner_organizing_use_recq | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the above configuration of "Send queue daemon partner organizing mechanism" is set to "database values", it's possible to active the check of the send queue for active partner connections. This amount of active connections will be added to the calculation of active connections for opening new connections during send queue daemon handling. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Should Seon send queue daemon unblock all blocked entries on startup? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || seonsqd_unblock_on_start | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The default behaviour of Seon send queue daemon on startup: if enabled, the daemon unblocks all blocked send queue entry for the configured server ID. The behaviour up to 2007-11-24 was like enabling this feature. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Enable offline handling of OFTP2 transfered files? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || offline_oftp2_filehandling | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since version 2007-12-01, Seon is able to handle OFTP 2 offline, so the security features of OFTP2 can be used in an insecure network segment. Enable this feature in order to use [[seon_oftp2_offlinehandling]] to handle the received files semi-manually. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== pre-script for offline tool ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || offline_oftp2_pre_script | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | This script is executed before the handling process starts. It may be used to transfer the file itself from one location to another. Parameters are documented [[Seon oftp2 offlinehandling#pre-script|here]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== post-script for offline tool ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || offline_oftp2_post_script | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | This script is executed after the handling process starts. It may be used to clean up the environment. Parameters are documented [[Seon oftp2 offlinehandling#post-script|here]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== remove successfully handled offline OFTP2 file entries ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftp2_offlinefile_remove_entries | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If this flag is enabled, successfully handled files will be removed from the list of received files. It's highly recommended to turn this flag on. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Identify remote partner via incoming medium, too? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || partner_search_medium | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | When enabled, the Seon receive daemon checks for the given medium the partner connects to the server and identifies the partner with this information in addition to the given SSID and password. This feature is very handy when several partner entries with the same SSID and password exist for different reasons. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Don't send EERP messages immediately in OFTP 1.x sessions? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || no_instant_eerp | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | When enabled, Seon doesn't send instantly EERP (end-to-end-response) messages to the remote partner containing the default parameters. If enabled, you have to create the EERP message manually (or programatically) in order to be sent correctly to the partner. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Receive all files if partner is authentificated?==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || receive_catch_all | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | In order to receive '''ALL''' files of a authenticated partner (via SSID and password), without any check of locally defined originator and/or destination SFID, please active this checkbox. All files are being received without any error, even if no partner has been configured for this configuration of SFIDs. You should design your post-processing of the received file via the "[[Seon_Core_event_scripts#end_receive_script|end receive script]]" on your own. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Cleanup queues on daemon startup? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || cleanup_queues | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If enabled, a successful start of a send or receive queue daemons cleans up the respective queue with the following rules: | ||
| + | *server ID matches the started daemon | ||
| + | *send queue daemon "<code>seonsqd</code>": Reset all files in status "taken by send queue" and "send in progress" to "new in queue" | ||
| + | *receive queue daemon "<code>seonrd</code>": Remove all files with the same server ID | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because it's a quite destructive option, the default is ''off''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Should invalid restart positions deactivate restart of file? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || dont_restart_invalid_offset | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If enabled, all files given with a restart position bigger than proposed file size won't restart file transfer and begin at the start of the file (i.e. if file size is 44123kB, but restart position is available at 49876kB, because the physical file is 51832kB big; received file size is bigger that the proposed 44123kB because the file '''is''' bigger). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Note:'' Volvo needs this flag to be turned on in special conditions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Activate OFTP2 secure authentification directly after certificate delivery? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || activate_ssidauth_after_delivery | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If enabled, the partner switch "use OFTP2 secure authentification" will be enabled right after an automatic import of a certificate delivery. | ||
| + | Please note that this may influence the behaviour of new connections: they may be aborted if the configuration flag [[Seon_Core_configuration#allow_unsecure_OFTP_2_authentification|allow unsecure OFTP 2 authentification]] is disabled and this partner wants to connect the next time and doesn't have the same settings activated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Enable per-partner virtual file naming recognition? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || per_partner_sfiddsn | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If enabled, an incoming file will be checked against a list of configured partner entries with the configured SFID (originator and destination) and in addition to this normal behaviour, against a list of configured virtual filenames (so-called "DSN", "Virtual File '''D'''ata'''s'''et '''N'''ame" or "SFIDDSN"). These allowed virtual filenames are configurable at a per-partner basis, so they are an additional switch which partner entry is handling this special filename. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If multiple partner entries match, first one will be used. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Fetch EERPs? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configDaemonFetchEerp | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If enabled, Seon's send queue daemon will contact the remote partner for every file which is in the send queue status "waiting for remote acknowledge". In the newly created session, the partner has the chance to send the EERP or NERP message for any file. | ||
| + | The maximum amount of configured sessions for a partner is being used (if available and configured properly in the "partner table" configuration). No more than the maximum of this amount of sessions will be opened, summarized for poll queue, send queue files and EERP fetching entries. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Fetch EERPs every x timeslice ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configDaemonFetchEerpTimeslice | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If EERP fetching is enabled, this factor is being used to increase the time between two connect tries of the Seon send queue daemon when trying to fetch one or more EERP messages of a partner. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Fetch EERPs for ISDN partners, too? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configDaemonFetchEerpIsdnToo | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since 2016-11-28, by default Seon only fetches EERPs for TCP/IP and TLS partners (before this release, also ISDN partners are being contacted for missing EERPs). If you activate this checkbox, also ISDN partners are being contacted for missing EERPs (files in the send queue with status "waiting for remote acknowledge). '''Be aware that in combination with the send queue daemon time slice parameter and the EERP timeslice factor, the send queue daemons initiates outgoing sessions which can generate connection costs!''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Don't deactivate dir.scanner entries on error? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configDaemonDirscannerDontDeactivate | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If enabled, the send queue daemon will not deactivate diresctory scanner entries if an error occurs with the according enttry (i.e directory not available, permission errors etc.). By default, this configuration option is disabled and the daemon will deactivate such entries, logging this in the system logs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Allow underscore character ("<code>_</code>") in virtual filenames? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configDaemonAllowUnderscoresInVirtFilenames | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Some OFTP and OFTP2 systems out in the wild support the underscore character in virtual filenames, which is unsupported by the RFC. In order to support this common mistake of standard interpretation, Seon supports this non-standard character in addition to the well-defined characters, which are: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | The numerals: 0 to 9 | ||
| + | The upper case letters: A to Z | ||
| + | The following special set: / - . & ( ) space | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Seon Enterprise === | ||
| + | The behaviour of Seon Enterprise can be influenced in the following three topics: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Config-Enterprise.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Seon Enterprise - Basic ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== is Seon Enterprise installed? ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || seon_enterprise | ||
| + | |} | ||
If you enable this checkbox, the web interface expands its funtionality needed to administrate Seon Enterprise, an enhanced version of Seon. Disabling this checkbox | If you enable this checkbox, the web interface expands its funtionality needed to administrate Seon Enterprise, an enhanced version of Seon. Disabling this checkbox | ||
turns Seon into its default configuration of Seon Core. If you are interested in features of Seon Enterprise, contact your software dealer or write an email to info@seon.de . | turns Seon into its default configuration of Seon Core. If you are interested in features of Seon Enterprise, contact your software dealer or write an email to info@seon.de . | ||
| − | === | + | ===== default country ===== |
| − | The | + | {|style="background:white" |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || default_country_idx | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | When creating a new company entry in the Seon partner database and using Seon Enterprise, a country has to be selected for this partner. For easy administration, a default country is configurable with with configuration. This configuration is only visible if Seon Enterprise is installed (and the above checkbox is enabled). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== default receive plugin group ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || default_rec_plugin_pkg | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | This pulldownmenu contains all defined plugin packages. You should select a plugin package which will be run after a job is completely received (i.e. after the receive file sorter has collected all needed files). This configuration is only visible if Seon Enterprise is installed (and the above checkbox is | ||
| + | enabled). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== default send plugin group ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || default_send_plugin_pkg | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The configured default send plugin group is used to pre-configure a plugin group which is used for newly added partners. This plugin group will be configured at company level (the highest hierarchy level) for the new partner. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== enable multi-protocol support? ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || seon_enterprise_other_protocols | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | In order to enable other protocols in addition to OFTP and OFTP2 (which is handled via the Seon send queue for outgoing files), you may define and use other protocols for data transfer to partners. Enable this checkbox to get more options on then. See [[Seon Enterprise - other protocols]] for more details about administration. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== define own company ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || seon_enterprise_own_company | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | For a finer grained target address code search, you can define your own company here. If "no selection - enable multi-client-support" is selected, all address codes of all companies will be used for recipient search. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Default recipient for incoming jobs ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || enterprise_default_rec | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | By default, no recipient is configured for inomcings jobs in initial state. By defining a default recipient here, this person will be defined as the initial recipient, leading to an execution of the configured plugin group of this recipient if no other plugin changes this recipient successfully. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Path for jobs of directory scanner ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || enterprise_dirscanner_jobdir | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | This name defines the path (relative to the [[Seon_Core_configuration#data_outgoing_directory|outgoing directory]]) wherein the directory scanner will create jobs. The job number will be appended to this given directory name. Relative path information can be used, too (using "../" definitions). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Examples (with a default [[Seon_Core_configuration#data_outgoing_directory|outgoing directory path]] of "<code>/opt/seon/outgoing</code>"): | ||
| + | *definition: <code>seon-dirscanner-enterprise-job-</code> | ||
| + | *resulting path (for job 123): <code>/opt/seon/outgoing/seon-dirscanner-enterprise-job-123/</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Enable auto-addresscode functionality ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || enterprise_auto_adrcode | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | When enabled, editing a recipient adds the ability to create a new unique address code, based on values of other persons in that company. The algorithm tries to identify a numeric element of the existing address code and increments it until an unused value is available. This functionality may fail for address codes without a numeric element. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Enable addresscode uniqueness checks ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || enterprise_unique_adrcode | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | When enabled, the administrative web interface warns an administrator if the configured address code is used by another person in the same company. This is done by marking the input field as invalid, adding a hover mask for a textual information that this address code is used already. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Disable automatic addresscode conversion ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configGuiAddresscodeDontConvert | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | When enabled, the administrative web interface doesn't convert the addresscode into upper case, so it's usable for other purposes than ENGDAT routing. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Shall errornous sendings abort jobs ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configEnterpriseAbortJobRejectedFiles | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | When enabled, the "end send" event of Seon Core will abort jobs if sending is errornous. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Absolute AJAX URL for job restore processes ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || enterprise_archive_restore_url | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | For archived jobs, this URL will be called via JSONP in order to restore the job. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Name of parameter for restore AJAX call ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || enterprise_archive_restore_parametername | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | When restoring Seon Enterprise jobs via the above configured URL, this is the name of the parameter containing the archive ID. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Event to be executed for sent non-Enterprise files ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || non_enterprise_send_event | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you use Seon Core and Seon Enterprise events in parallel, this event will be fired if a "end_send" will be executed for non-Enterprise enqueued files. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Name of JSONP callback parameter ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || enterprise_archive_restore_callbackname | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Due to JSONP, this is the name of the required callback function parameter. The default value (if empty) is "<code>callback</code>". | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Seon Enterprise - Webaccess ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Webaccess login logo URL ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || webaccess_login_logo | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | An alternative logo URL (absolute or relative is supported) for displaying in the login prompt of Seon Webaccess. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Webaccess logged in logo URL ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || webaccess_loggedin_logo | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | When defined, a customized logo can be added to the logged-in view of Seon Webaccess in the top right corner. Absolute or relative URLs are supported. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Encrypt Webaccess session information ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || webaccess_session_encrypt | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If required, Seon Webaccess can encrypt the session information in the database via AES256 algorithm and hashed via SHA1 hashing algorithm. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Compress Webaccess session information ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || webaccess_session_compress | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If required, Seon Webaccess can compress the session information in the database via bzip2 algorithm. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Don't show receive queue view ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || webaccess_disable_recq | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | If you don't want the receive queue to be displayed to end-users in Seon Webaccess, enable this checkbox. The receive queue view doesn't contain any administrative operations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Don't show send queue view ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || webaccess_disable_sendq | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | If you don't want the send queue to be displayed to end-users in Seon Webaccess, enable this checkbox. The send queue view doesn't contain any administrative operations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Show incoming jobs without recipient ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || webaccess_show_invalid_rec_jobs | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | When enabled, this feature adds jobs without a valid recipient to the list of incoming jobs for all users. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Session timeout (min) ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || webaccess_session_timeout | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | You can set a session for timeout for Seon Webaccess sessions here. Without any interaction, an old session expires automatically after that amount of minutes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Highlight address code in ENGDAT filenames ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || webaccess_highlight_addresscode | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | If ENGDAT filenames are not interpreted into real filenames (as given i.e. in ENGDAT abstract files, these files are quite technical to read. In order to highlight the address code contained in the filename, enabling this configuration options offers to highlight this address code with the following methods: | ||
| + | *bold (configuration variable "<code>webaccess_highlight_addresscode_bold</code>") | ||
| + | *underlined (configuration variable "<code>webaccess_highlight_addresscode_underline</code>") | ||
| + | *italic (configuration variable "<code>webaccess_highlight_addresscode_italic</code>") | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Show all incoming jobs of department ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || webaccess_show_dep_jobs_incoming | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Seon Webaccess normally shows only jobs of the corresponding user who is logged in. In order to show all incoming jobs of the department the user is contained, enable this checkbox. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Show all outgoing jobs of department ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || webaccess_show_dep_jobs_outgoing | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | Seon Webaccess normally shows only jobs of the corresponding user who is logged in. In order to show all outgoing jobs of the department the user is contained, enable this checkbox. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Include given name in search ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || webaccess_search_given_name | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | When searching for persons in Seon Webaccess (in any situation), the given name (aka. the "first name") is not searched for by default. By enabling this configuration option, searching for the given name is being activated, too. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Don't show popup when adding recipient ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || webaccess_ignore_recipient_add | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | When adding a new recipient to a send job, a popup occurs when not enabled. If enabled, no popup will occur. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Seon Enterprise - Plugins ==== | ||
| + | The default behaviour of all plugins can be changed here. The behaviour can be overridden by a configured, set up at each level of partner hierarchy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | === OFTP2 === | ||
| + | OFTP2 relevant options are configurable here: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Config-OFTP2.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== delete temporary created files of OFTP 2 session ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftpv2_delete_temp_created_files | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If enabled (all other values than zero, '<code>0</code>') all files created for temporary usage in OFTP2 sessions and session preparations will not be deleted. This is useful for debugging the created files and meta-information. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Enable offline handling of OFTP2 transfered files? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || offline_oftp2_filehandling | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If enabled (all other values than zero, '<code>0</code>') incoming OFTP2 files (which need to be handled by any security mechanism, such as signature checking, decompression and/or decryption, will be held in an offline queue, which will then be evaluated by the Seon offline daemon. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== pre-script for offline tool ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || offline_oftp2_pre_script | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If OFTP2 offline handling is enabled, you may enter here the absolute path to an executable which will be executed by the Seon offline handler before the offline handler processes the file. This is normally a transferer script. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== post-script for offline tool ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || offline_oftp2_post_script | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If OFTP2 offline handling is enabled, you may enter here the absolute path to an executable which will be executed by the Seon offline handler after the offline handler has processed a file. This is normally a cleanup script. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== remove successfully handled offline OFTP2 file entries ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftp2_offlinefile_remove_entries | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If OFTP2 offline handling is enabled, successfully processed files will be removed from the offline queue (the database table only, not from the filesystem!) if this feature is activated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Activate OFTP2 secure authentification directly after certificate delivery? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || activate_ssidauth_after_delivery | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If enabled, Seon activates secure authentification method for the given partner right after an automatic certificate exchange. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Don't send EERP messages immediately in OFTP2 sessions? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || no_instant_oftp2_eerp | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | After successful receipt of an OFTP2 file, you may suppress the automatic sending of an EERP by activating this feature. You should ensure to send an EERP via "[[Seon_Core_binaries#seoneq_.2F_seoneq2|seoneq]]" with all parameters given in the "[[Seon_Core_event_scripts#end_receive_script|end receive script]]". | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Send EERP in synchronous session? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configOftp2SyncEerp | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | In OFTP2, file handling (like decompression, signature verification and decryption) is being processed in an asynchronous, forked process (because this handling can take a very long time in terms of network connections; many minutes are not uncommon). If you have to deal with synchronous data transfers where an EERP '''MUST''' be transfered in the same OFTP2 session, you can enable this option. Beware of the (default: 1MB) size limit of received files for enabling this feature. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Maximum size of sync. EERP files (in kB) ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configOftp2SyncEerpMaxsize | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the above mentioned synchronous EERP handling for OFTP2 is enabled, you have to define a filesize limit of the transfered file. Files bigger that this limit are not handled by the synchronous EERP process. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Add log entry for synchronous EERP handling ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configOftp2SyncEerpLog | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If synchronous file handling takes place, an optional log entry can be places in the receive log every time this process is activated. '''Warning:''' may increase your receive log massively! | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Delete original OFTP2 handled files which have been enqueued by send queue daemon? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || deleteToBeEnqueuedTouchedFiles | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If a file, which has been in status 10 ("''to be enqueued for OFTP2''"), may result in a temporary OFTP2 file if one of the options for OFTP2 file handling is enabled (compression, signing or encryption). If this is the case, the original file would stay in it's original state. When enabling this feature, Seon deletes this original file for security reasons from the filesystem. '''WARNING: no undo or recovery is available!''' | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== OFTP2 security policy ==== | ||
| + | Starting with Seon release 2016-08-16, you can define which security settings match your internal company security policy with easy-to-answer configurations. The following parameters help to configure these values in an easy way. These settings are only relevant for the reception of files, sending files with another settings is possible nevertheless with potentionally different partner settings. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following configuration options can be defined to a behaviour explained below: | ||
| + | *File encryption (dabase configuration name: "<code>oftp2_policy_encrypted</code>") | ||
| + | *File compression (dabase configuration name: "<code>oftp2_policy_compressed</code>") | ||
| + | *File signature (dabase configuration name: "<code>oftp2_policy_signed</code>") | ||
| + | |||
| + | The configuration options explained: | ||
| + | *unconfigured: All files are accepted | ||
| + | *Allow: All files are accepted, both with activated and deactivated security option. | ||
| + | *Require: The security option '''MUST''' be activated for incoming files, otherwise the file will be rejected with an appropriate error message. | ||
| + | *Reject: The security option '''MUST NOT''' be activated for incoming files, otherwise the file will be rejected with an appropriate error message. | ||
| + | *Require partner value: Require partner value: The file must be sent by the remote party according to the settings which are activated or deactivated in your partner configuration. If the security option is not fulfilled, the file will be rejected with an appropriate error message. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If a security policy is not fulfilled, an offered file will be rejected. A log entry in the receive log will occur per file. The partner is given the information not to retry this sending process again. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Allow fallback to unsecure OFTP 2 authentification ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftpv2_allow_unsecure_auth | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If enabled (all other values than zero, '<code>0</code>') it is possible to connect to Seon with a disabled secure authentification mechanism, even if the identified partner (via SSID and password) has a secure authentification method activated. If this configuration is disabled (which is the default), OFTP2 sessions are directly closed with a secure session error message. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Preferred cipher suite ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftp2_policy_preferred_cs | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | This configured cipher suite will be the preferred one for incoming files. With the option below, files using another cipher suite can be rejected. The list of cipher suites is dynamically obtained from the OFTP2 system. If the configuration value is "Use partner configured value", incoming files shall (or must, depending on the option below) be using the cipher suite which is defined at partner level. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Deny other cipher suites than the preferred ===== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftp2_policy_deny_unpreferred_cs | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If a ciphersuite is configured in "Preferred cipher suite" and incoming files use another cipher suite, this option will reject the incoming file with an appropriate error message. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== External IP address or hostname of this OFTP2 system ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftp2_external_hostname | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | This configuration option is used in new certificate signing requests as the common name ("CN") of this OFTP2 system. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Activate auto-cleanup of old certificates? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configOftp2AutoCleanup | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since certificates will expire, Seon will warn you about this fact. If you want Seon to clean up expired certificates automatically (so you don't have to do this manually), you can enable this checkbox. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Automatically enable disabled certificates? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || configOftp2AutoEnableInactiveCert | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If an old certificate has been archived by the mechanism above, disabled (say: not yet enabled) certificates can be enabled dynamically. This is also a mechanism for automatic handling during certificate renewal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Logging === | ||
| + | Logging enables Seon to insert human readable messages into log tables. You may turn some features on or off to suite your needs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Config-logging.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== use syslog ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || use_syslog | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you turn on this checkbox, major errors will be logged to the server's syslog facility with the severity LOG_ERR. Major errors are table misconfigurations or process dependant messages (fork failures, memory allocation problems etc.). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== enable log vault ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || enable_log_vault | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Enabling this feature activates code to move log entries from the direct access log tables to slower log vault tables, where all messages (older than a configurable amount of days) are kept. This enhances the access to the online logs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== maximum age for fast logs ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || logvault_days | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | After this amount of days, log entries will be moved from one log to the vault. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== move send logs every x timeslices ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || logvault_sendq_timeslices | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The entries older than the above configured value ('maximum age') of the send log will be moved to the slower vault every this amount of time slices of the send queue daemon. This configuration value cooperates with the configuration value 'time slice for send queue daemon'. Only logs belonging to that server ID will be moved to the vault! | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== move receive logs every x timeslices ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || logvault_recq_timeslices | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The entries older than the above configured value ('maximum age') of the receive log will be moved to the slower vault every this amount of time slices of the receive queue daemon. This configuration value cooperates with the configuration value 'time slice for receive daemon'. Only logs belonging to that server ID will be moved to the vault! | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== archive received xERP messages & archive sent xERP messages ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || oftpv2_archive_received_xerp & oftpv2_archive_sent_xerp | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | It may be useful archive positive and/or negative end-to-end responses. These xERP messages can be seen as acknowledgements from the partner (received xERP) or from | ||
| + | yourself (sent xERP). The web interface contains a archive viewer on the left hand: "xERP log". This feature may be needed in some countries for legal issues. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== enable script logging ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || enable_script_logging | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Enabling this feature logs all script calls, parameters, returncodes and output to the script logs. In the web interface, you can take a look at the script logs with the link „Script log“. In this interface, you can also restart event scripts (even if they have changed in the configuration: you can then execute the original or the new one, depending on executability of the script file). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Enable directory scanner logging? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || enable_dirscanner_logging | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If enabled, the [[Seon Directory Scanner|directory scanner]] logs every single execution script based on the found file. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Enable continuous write of Seon debug daemon output? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || seondebugd_continuous_write | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | When enabling this feature, the Seon debug daemon creates a debug log file (and starts the configured event script if existant) after the ring buffer is full. In this case, no message is lost. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If this feature is enabled, starting with Seon release 2015-08-25 a button with the label "Collect today's logs" is available which lets you send all collected debug daemon dump files of this day and enqueue it to a specific partner for debugging. Requirements for this feature are: | ||
| + | *Seon debug daemon is running | ||
| + | *The temporary directory is accessible and writable by the Seon debug daemon | ||
| + | *The event "debug daemon log event" does not change the filename prefix "seon-logfile-<YYYYmmdd>" (where "YYYY" is the current year with four digits, "mm" is the actual month starting at "01" with two digits and "dd" is the actual day, starting with "01" and two digits). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The partner to which the files are being enqueued is possible to be searched. By default, the partner "Seon-Update" is searched. If the partner is not found, no partner search is pre-set and the whole partner list is being presented. If exactly this pre-set partner "Seon-Update" is found, it it selected automatically, so you don't have to click on it to activate the selection. Only if a single partner is selected in the partner search list, the files are being enqueued to this partner after submission (either via "Save" button or via double click). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The virtual filenames of the logfiles is "Seon-LOGFILE-<counter>" where "<counter" is an incremented number, starting with 1 (one). The comment of the automatically enqueued files is "<code>Seon logs - automatically enqueued via administrative web interface</code>". | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Absolute path to logfile of Seon API ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || seonapi_logfile | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Seon API, which is the background service for Seon Webaccess and Seon Proxy, logs into this file. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Seon API loglevel ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || seonapi_loglevel | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The above configured file will be written in the configured log level. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Suppress unsuccessful connect log entries? ==== | ||
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || suppress_unsuccessful_connect_logs | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | If an incoming connection fails before OFTP handshake could be initiated, a logging entry is normally made in the style of: | ||
| + | unsuccessful connect try from IP 'aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd' | ||
| + | If you want to ignore these messages (i.e. when using a system monitoring which just watches if the TCP/IP port is open), enable this feature. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === GUI === | ||
| + | The GUI offers some parameters which influence the default behaviour. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:ConfigGui.png]] | ||
| − | + | ==== Send signals to running processes ==== | |
| + | {|style="background:white" | ||
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || webgui_kill_processes | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | The PHP backend can send running processes a signal, i.e. for reloading their configuration (when clicking "Save") or cancelling transfer processes. If the webserver is not running on the same machine as the Seon daemons do, or if the webserver user is not privileged to send signals to running Seon processes (i.e. they are running in another user context), you should disable this checkbox, otherwise (which is the default) keep it activated for a seamless integration of GUI and backend. | |
| − | |||
| − | ==== | + | ==== Disable PID check of daemons ==== |
| − | + | {|style="background:white" | |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || disable_PID_checks | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | The Seonapi can check if daemons which should run with a given process ID really exist. If they don't exist, the Seonapi will cleanup running information (= their PIDs) in the database. This feature is available in Linux and MacOS, partially in AIX. If you get unwanted results, disable this feature. | |
| − | |||
| − | ==== | + | ==== Show partners with unknown medium ==== |
| − | + | {|style="background:white" | |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || display_partners_with_unknown_medium | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | Since the configurable partner database schema is highly configurable, many partner entries may have an unknown transmission medium configured (valid values are configurable for ISDN, unencrypted TCP/IP and encrypted TCP/IP aka. TLS). If this configuration option is enabled, all partners (even with unknown medium values) are displayed in the partner list. | |
| − | |||
| − | ( | ||
| − | ==== | + | ==== Enable simple configuration ==== |
| − | + | {|style="background:white" | |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || simple_config_gui | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | In many installations, most complex situation are not needed for this installation. As a minimizer for unneeded configuration options, most uncommon configuration options are not visible when enabling this configuration option. Elements which are hidden when this config option is activated are: | |
| − | + | *Configuration: | |
| + | **TCP/IP | ||
| + | **ISDN | ||
| + | **Events | ||
| + | **Daemon | ||
| + | **OFTP2 | ||
| + | **Logging | ||
| + | **Partner table | ||
| + | *Programs: | ||
| + | **Partner import | ||
| + | *Cipher suites | ||
| − | + | Partner management for OFTP2 is also more easy, so a more or less incomplex system will be shown in order to allow non-common users to administrate the system well. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==== | + | ==== Min. age for expiration warning of certificates ==== |
| − | + | {|style="background:white" | |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || gui_cert_warning_days | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | The administrative web interface can show expiring certificate warnings and expired certificate errors in the tab "Welcome", section "Possible configuration problems". The configured amount of days are used for calculation which certificates to display. | |
| − | |||
| − | ==== | + | ==== Theme for administrative GUI ==== |
| − | + | {|style="background:white" | |
| − | + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | |
| − | + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || gui_theme | |
| − | + | |} | |
| − | + | The admin web interface supports the switch of the used theme for displaying information. You can switch the theme without saving dynamically. When saving this config, all subsequent calls to the web interface will switch to the configured theme. | |
| − | The | ||
| − | ==== | + | ==== Disable health check of database ==== |
| − | + | {|style="background:white" | |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || gui_disable_db_healthcheck | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | Disabling the database health check will not include database table checks in the section "Possible configuration option" in the "Welcome" tab of the administrative web interface. By disabling these checks, you can lower your database overhead massively. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ==== Filtered filesystems from "Welcome" tab ==== |
| − | + | The administrative web interface shows the filling state of all mounted filesystems, except the filesystems contained in the list of excluded filesystems. A filesystem can be exluded from the displayed list by clicking on the entry bar on the "Welcome" page, then answering "Yes" to the delete question. The deleted file system(s) are listed here in a grid, where they can be removed so the removed entry will be displayed again on the welcome page. | |
| − | ==== | + | ==== User own defined URLs ==== |
| − | + | {|style="background:white" | |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || use_own_defined_urls | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | If enabled, the menu on the left side in the administrative web interface will add an entry with a configured name (see below). | |
| − | |||
| − | ==== | + | ==== Name of entry ==== |
| − | + | {|style="background:white" | |
| + | |- style="background:lightgrey;" | ||
| + | | '''DB configuration name:''' || own_defined_urls_menuentry_name | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | The name of the menu entry which contains user-defined URLs is changeable. | |
| − | |||
| − | ==== | + | ==== Own defined URLs ==== |
| − | If | + | If enabled, the administrative web interface adds the possibility to configure a list of URLs for viewing within the administrative web interface as a closeable tabbed entry. The included URL is being integrated via an IFRAME, so if the integrated page doesn't allow this functionality (i.e. thorugh a META tag), the content will stay empty. Keep in mind that many popular dynamic sites don't allow this type of integration. Have a look into your JavaScript console if any errors occur. |
| − | === | + | === Send queue displayed columns === |
| − | + | The list of columns configure the default state of the columns when opening the send queue overview. The columns can be re-activated afterwards via the column header management. | |
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ---- |
| − | + | === other interesting configurable values === | |
| + | Some values are not configurable via web interface, but also have a useful meaning when running Seon. These configuration value names are: | ||
| + | *<code>seonclientd_port</code>: TCP/IP port of the program Seon client daemon | ||
| + | *<code>webinterface_path</code>: Absolute path of the web interface on the webserver. This is useful for upgrading processes in order to update the path correctly. | ||
Latest revision as of 13:07, 13 September 2018
Contents
- 1 Accessing configuration
- 2 Configurable values
- 2.1 TCP/IP
- 2.2 SSL/TLS parameters
- 2.2.1 TLS server certificate file & TLS server certificate password
- 2.2.2 TLS client certificate file file & TLS client certificate password
- 2.2.3 root certificate file & root certificate path
- 2.2.4 Diffie-Hellman parameter files
- 2.2.5 TLS server: check client certificate validity
- 2.2.6 Ignore TLS CRL unavailability?
- 2.2.7 Archive CRLs?
- 2.2.8 Disable automatic CRL handling
- 2.2.9 Disable automatic reactivation of CRLs
- 2.2.10 Check CRL URLs every x timeslices
- 2.2.11 Maximum age of CRLs
- 2.2.12 Entropy file for random data
- 2.2.13 TSL URL
- 2.2.14 Disable security warnings?
- 2.2.15 Enable only PFS ciphers?
- 2.3 Proxy
- 2.4 ISDN parameters
- 2.5 Odette parameters
- 2.6 Directories
- 2.6.1 data incoming directory
- 2.6.2 data outgoing directory
- 2.6.3 temporary directory
- 2.6.4 database backup directory
- 2.6.5 binary installation directory
- 2.6.6 script installation directory
- 2.6.7 absolute path to 'openssl'
- 2.6.8 absolute path to 'rrdtool'
- 2.6.9 RRDB data path
- 2.6.10 absolute path to RRDtool TTF file
- 2.6.11 SQL lost messages file
- 2.6.12 Append datestamp to SQL lost messages file?
- 2.6.13 MySQL dump tool
- 2.6.14 send test file
- 2.7 Events
- 2.7.1 event script usage
- 2.7.2 event script sleep time
- 2.7.3 start send script
- 2.7.4 end send script
- 2.7.5 xERP script
- 2.7.6 start receive script
- 2.7.7 end receive script
- 2.7.8 start session script
- 2.7.9 end session script
- 2.7.10 send queue entry blocked script
- 2.7.11 debug daemon log script
- 2.7.12 license script & trigger level
- 2.7.13 Enable automatic update mechanism & Seon automatic software update event
- 2.7.14 Seon automatic update post event
- 2.7.15 enqueue post-script
- 2.7.16 Seon API proxy system log event script
- 2.8 Daemon parameters
- 2.8.1 run Seon programs as user
- 2.8.2 run Seon update program as user
- 2.8.3 time slice for send queue daemon
- 2.8.4 time slice for receive daemon
- 2.8.5 delete send queue entries
- 2.8.6 Cleanup of sent send queue entries
- 2.8.7 let all files of send queue be fetchable
- 2.8.8 overwrite existing incoming files
- 2.8.9 default maximum send tries for send queue daemon
- 2.8.10 additional sleeping time for send queue daemon & additional sleeping time factor for send queue daemon
- 2.8.11 progress bar refresh time
- 2.8.12 allow unsecure OFTP 2 authentification
- 2.8.13 delete temporary created files of OFTP 2 session
- 2.8.14 local character set
- 2.8.15 Unblock blocked send queue entries after successful connect?
- 2.8.16 Disable file restart functionality?
- 2.8.17 Disable automatic database cleanups / optimizations?
- 2.8.18 enable OFTP message checker
- 2.8.19 send queue entry status after abort
- 2.8.20 enable statistics & RRDtools refresh time
- 2.8.21 Append timestamp to received file
- 2.8.22 Append destination SFID to received file
- 2.8.23 Append PID of receive process to received file
- 2.8.24 OFTPv1: Don't wait for EERP message
- 2.8.25 Enable automatic update mechanism?
- 2.8.26 Send queue daemon partner organizing mechanism
- 2.8.27 Should Seon send queue daemon unblock all blocked entries on startup?
- 2.8.28 Enable offline handling of OFTP2 transfered files?
- 2.8.29 Identify remote partner via incoming medium, too?
- 2.8.30 Don't send EERP messages immediately in OFTP 1.x sessions?
- 2.8.31 Receive all files if partner is authentificated?
- 2.8.32 Cleanup queues on daemon startup?
- 2.8.33 Should invalid restart positions deactivate restart of file?
- 2.8.34 Activate OFTP2 secure authentification directly after certificate delivery?
- 2.8.35 Enable per-partner virtual file naming recognition?
- 2.8.36 Fetch EERPs?
- 2.8.37 Fetch EERPs every x timeslice
- 2.8.38 Fetch EERPs for ISDN partners, too?
- 2.8.39 Don't deactivate dir.scanner entries on error?
- 2.8.40 Allow underscore character ("_") in virtual filenames?
- 2.9 Seon Enterprise
- 2.9.1 Seon Enterprise - Basic
- 2.9.1.1 is Seon Enterprise installed?
- 2.9.1.2 default country
- 2.9.1.3 default receive plugin group
- 2.9.1.4 default send plugin group
- 2.9.1.5 enable multi-protocol support?
- 2.9.1.6 define own company
- 2.9.1.7 Default recipient for incoming jobs
- 2.9.1.8 Path for jobs of directory scanner
- 2.9.1.9 Enable auto-addresscode functionality
- 2.9.1.10 Enable addresscode uniqueness checks
- 2.9.1.11 Disable automatic addresscode conversion
- 2.9.1.12 Shall errornous sendings abort jobs
- 2.9.1.13 Absolute AJAX URL for job restore processes
- 2.9.1.14 Name of parameter for restore AJAX call
- 2.9.1.15 Event to be executed for sent non-Enterprise files
- 2.9.1.16 Name of JSONP callback parameter
- 2.9.2 Seon Enterprise - Webaccess
- 2.9.2.1 Webaccess login logo URL
- 2.9.2.2 Webaccess logged in logo URL
- 2.9.2.3 Encrypt Webaccess session information
- 2.9.2.4 Compress Webaccess session information
- 2.9.2.5 Don't show receive queue view
- 2.9.2.6 Don't show send queue view
- 2.9.2.7 Show incoming jobs without recipient
- 2.9.2.8 Session timeout (min)
- 2.9.2.9 Highlight address code in ENGDAT filenames
- 2.9.2.10 Show all incoming jobs of department
- 2.9.2.11 Show all outgoing jobs of department
- 2.9.2.12 Include given name in search
- 2.9.2.13 Don't show popup when adding recipient
- 2.9.3 Seon Enterprise - Plugins
- 2.9.1 Seon Enterprise - Basic
- 2.10 OFTP2
- 2.10.1 delete temporary created files of OFTP 2 session
- 2.10.2 Enable offline handling of OFTP2 transfered files?
- 2.10.3 Activate OFTP2 secure authentification directly after certificate delivery?
- 2.10.4 Don't send EERP messages immediately in OFTP2 sessions?
- 2.10.5 Send EERP in synchronous session?
- 2.10.6 Maximum size of sync. EERP files (in kB)
- 2.10.7 Add log entry for synchronous EERP handling
- 2.10.8 Delete original OFTP2 handled files which have been enqueued by send queue daemon?
- 2.10.9 OFTP2 security policy
- 2.10.10 External IP address or hostname of this OFTP2 system
- 2.10.11 Activate auto-cleanup of old certificates?
- 2.10.12 Automatically enable disabled certificates?
- 2.11 Logging
- 2.11.1 use syslog
- 2.11.2 enable log vault
- 2.11.3 maximum age for fast logs
- 2.11.4 move send logs every x timeslices
- 2.11.5 move receive logs every x timeslices
- 2.11.6 archive received xERP messages & archive sent xERP messages
- 2.11.7 enable script logging
- 2.11.8 Enable directory scanner logging?
- 2.11.9 Enable continuous write of Seon debug daemon output?
- 2.11.10 Absolute path to logfile of Seon API
- 2.11.11 Seon API loglevel
- 2.11.12 Suppress unsuccessful connect log entries?
- 2.12 GUI
- 2.12.1 Send signals to running processes
- 2.12.2 Disable PID check of daemons
- 2.12.3 Show partners with unknown medium
- 2.12.4 Enable simple configuration
- 2.12.5 Min. age for expiration warning of certificates
- 2.12.6 Theme for administrative GUI
- 2.12.7 Disable health check of database
- 2.12.8 Filtered filesystems from "Welcome" tab
- 2.12.9 User own defined URLs
- 2.12.10 Name of entry
- 2.12.11 Own defined URLs
- 2.13 Send queue displayed columns
- 2.14 other interesting configurable values
Accessing configuration
Seon stores its core configuration in one simple database table. The configuration can therefor be changed in two ways:
- using the comfortable web interface
- using a database client program to change the values manually.
Because of the quite non-understandable names of the configuration values, all configuration value names are listed in each block of configuration for manual editing.
web interface method
The Seon web interface includes an entry in the left menu for the core configuration. Its name is "Configuration". The configuration web interface is segmentated into the following blocks:
- TCP/IP
- SSL/TLS
- ISDN
- Odette
- Directories
- Events
- Daemon
- Partner table
- GUI
Each block is accessible with a link in the head of the configuration panel.
database method
The table "[tableprefix]configuration" (default: "seon_configuration") contains two columns:
- name
- value
The column "name" is the name of the configuration which is affected.
The column "value" reflects the configuration value, limited to 255 characters.
All boolean values react that the a value of zero ("0") if false and all other values are true.
Configurable values
Seon is highly configurable. The following configuration parameters show the position in the web GUI, beginning in the top. Each configuration name as used in all binaries, web interface, scripts etc. are listed in each block and explained as needed.
TCP/IP
This block contains all basic TCP/IP parameters, such as port numbers, timeout values etc.
TCP/IP port of OFTP server
| DB configuration name: | tcp_port |
This numeric value between 1 and 65535 describes the TCP/IP port the OFTP server is watching for incoming connections. The maximum of parallel incoming connections is limited by the operating system kernel and can be influenced by the kernel parameter "SOMAXCONN".
TCP/IP port of OFTP server (TLS)
| DB configuration name: | tcp_port_tls |
This numeric value between 1 and 65535 describes the TCP/IP port the OFTP server is watching for incoming OFTP2 connections which are secured by TLS. The maximum of parallel incoming connections is limited by the operating system kernel and can be influenced by the kernel parameter "SOMAXCONN". This port must not be the same as the OFTP server port from above.
TCP/IP port of Seon debug daemon
| DB configuration name: | debugd_port |
This numeric value between 1 and 65535 describes the TCP/IP port the OFTP server is watching for debug output. Every Seon program generates this output. The daemon collects this data and is able to dump this data in an encrypted file. This must not be the same as OFTP or OFTP 2 server ports.
TCP/IP timeout
| DB configuration name: | tcp_timeout |
This numeric value defines the maxmimum number of seconds between two TCP/IP packages to arrive. If this value is too low you might get network disconnects, setting this value very high means that a network disconnect will be discovered very late.
TCP/IP OFTP maximum buffersize
| DB configuration name: | oftp_default_buffersize_tcpip |
During the OFTP handshake, the maximum size of a data buffer will be commited. This value reflects the maximum size of such data buffers. The minimum value is 128, the maximum can be should not be over 65535 (because of TCP/IP packaging). The higher the value, the faster the data transfer rate will be (but it depends on the partner side). On unreliable connections, use the default value of 2048 bytes. For configurations with problemous partners like old Seeburger products, please use 800 bytes as buffersize.
TCP/IP OFTP maximum credit count
| DB configuration name: | oftp_default_creditcount_tcpip |
As the OFTP maximum buffersize, this value will be commited with the partner during a OFTP handshake. The number defines the amount of uncommited data buffers send to the receiver during file transfers. Increasing this value also increases the throughput. On unreliable connections you should use the default of 20. This is a different value than used for ISDN connections. For configurations with problemous partners like old Seeburger products, please use 20 as credit count.
SSL/TLS parameters
For securing TLS sessions over TCP/IP networks (such as internet), you need to give some information about your local certificates. These information don't have to be the same as for file based security.
TLS server certificate file & TLS server certificate password
| DB configuration name: | tls_local_certificate & tls_server_cert_password |
Absolute path to the OFTP server certificate (in PEM format) for OFTP over TCP/IP (TLS secured). If the certificate is password-protected, you may enter it in the password field.
TLS client certificate file file & TLS client certificate password
| DB configuration name: | tls_default_client_certificate & tls_client_cert_password |
Absolute path to the OFTP server certificate (in PEM format) for OFTP over TCP/IP (TLS secured). If the certificate is password-protected, you may enter it in the password field.
root certificate file & root certificate path
| DB configuration name: | tls_root_certificate & tls_root_certpath |
The root certificates are used to authentificate partners which have certificates of unknown signers. At least one of these fields must be filled (even if the root certificate path doesn't contain any root certificates). The certificates must be in PEM format.
These variables are (if set) available to processes started by Seon via the environment variables "CA_FILE" and "CA_PATH" (see also Seon Core environment variables).
Diffie-Hellman parameter files
| DB configuration name: | dh128_file, dh256_file, dh512_file & dh1024_file |
These files (128bit, 256bit, 512bit and 1024bit) contain prime numbers, which are the basis for TLS encrypted connections. If the file is writable, or the file doesn't exist and the directory is writable, you can generate a new file from the web interface by using the link "Recalculate" or "Generate" in the web interface, which opens a new window which executes the command. Don't close this window until you can read the message "You can close this window now"!
TLS server: check client certificate validity
| DB configuration name: | tls_server_check_client_cert |
When this option is activated, all incoming TLS connections will be checked for a client certificate and a validity path for them. In case of self-signed certificates from the client, you have to add them manually (by requesting them from the partners) to your trusted certificate pool.
In case of client sessions, Seon will override a wrong purpose of the server certificate (such as "SSL client: no").
Summarizing:
If you have this checkbox enabled (default):
- Seon's TLS server asks the remote side, if not already presented, during TLS handshake for a client certificate.
- This TLS client certificate is checked against the list of trusted certificates in order to verify a valid certificate chain for the certificate.
- If the certificate chain is trusted, all chain elements are checked against the actually installed certificate revocation lists ("CRLs").
If you have this checkbox disabled (not the default, not recommended):
- None of the above checks is being executed.
- Every TLS client can connect to your server without any further client certificate check.
- Recommended only if:
- You have a firewall which applies partner defined rules, so you are sure who is connecting to your TLS server
- Have OFTP2 secure authentification enabled, in addition with the enabled "OFTP message checker" (in "Configuration" -> "Daemon") for protocol syntax validity verification (which lowers throughput and consumes higher server CPU).
| DB configuration name: | tls_ignore_crl_unavailable |
If the above option "check client certificate validity" is activated, it is possible to deactivate the check of an existance of a CRL for all CA certificates which Seon doesn't have a CRL downloaded yet. This solves the problems with the following log entries the system log:
TLS error: no X509 certificate given in TLS handshake by remote partner
openSSL error: TLS network session failed, certificate problem: application verification failure
You must download a CRL for the CA of the certificate with the subject '...'
certificate verify error 3: unable to get certificate CRL: depth=0, subject: ...
Archive CRLs?
| DB configuration name: | archive_crl |
When activated, all overwritten CRLs will be archived before every update. When deleting CRLs, they will be archived, too.
Disable automatic CRL handling
| DB configuration name: | disable_auto_crl |
Normally, the Seon send queue daemon scans all partner certificates for a new CRL URL and add them to the CRL list when not included. By activating this checkbox, you can disable this default behaviour.
Disable automatic reactivation of CRLs
| DB configuration name: | crl_dont_automatic_reactivate |
If automatic CRL handling is not deactivated, Seon will enable all found disabled CRL entries found in certificates. If you don't want this behaviour, you can disable the reactivation by enabling this configuration option.
Check CRL URLs every x timeslices
| DB configuration name: | autocrl_sendq_timeslices |
The send queue daemon can process every configured amount of timeslices (configured in the daemon section here) all trusted certificates and their CRL distribution points. If any is not included in the revocation list yet, it will be added and handled. Cofiguration values above 512 and below 1 will be resetted to 10.
Maximum age of CRLs
| DB configuration name: | maximum_crl_age |
CRLs carry a date within them which defined when they become invalid. Seon takes care of such CRLs by downloading and updating the database values according to the new content. With this configuration parameter you make any CRL entry invalid (and therefore marked for automatic update) which has an older update date than these amount of days before. So, the locally downloaded version of the CRL becomes invalid and gets updated eventually even before the next CRL will be issued.
This feature is recommended by the OFTP2 working group.
Entropy file for random data
| DB configuration name: | tls_entropy_file |
In order to use TLS, you have to specify a random data source. This is a kernel based character file (like "/dev/urandom" or "/dev/random"). If your operating system doesn't support such a random file (like AIX 5.1), you can generate such a file on your own (i.e. with the tool "ssh-rand-helper" from any openSSL installation). At least 256 bytes of random data must exist in this file.
TSL URL
| DB configuration name: | TSL_URL |
This URL defines the position of a list administrated by Odette which contains a list of authorized certificate authorities. If the signed XML could be verified successfully, all contained certificate authorities are added automatically to Seon.
The default value is:
http://www.odette.org/TSL/TSL_OFTP2.XML
Disable security warnings?
| DB configuration name: | configTlsDisableSecurityWarnings |
When enabled, Seon will never complain about insecure TLS cipher usage in connection logs (despite Seon SmartProxy logs, since the Seon SmartProxy doesn't support this insecurity "feature").
Enable only PFS ciphers?
| DB configuration name: | configTlsEnablePfs |
When enabled, all incoming and outgoing TLS traffic will occure with a secure TLS cipher supporting a secure key exchange mechanism. A fallback to a less secure cipher is supported, but logged.
Proxy
Seon offers for all HTTP and HTTPS transfer tasks proxy support. In order to use a defined proxy, several options are available. More details can be found here
Use HTTP proxy?
| DB configuration name: | proxy_enabled |
If you want to use a proxy, enable this checkbox. If the checkbox is disabled, all proxy relevant environment variables (see Seon HTTP Proxy support) are cleared in all proxy using tools and binaries (and thus the forked processes by these binaries also don't have proxy environment variables defined).
Use user settings/environment variables?
| DB configuration name: | proxy_use_env |
If your used running Seon already has environmental variables defined for proper proxy support, you should enable this checkbox. Otherwise (if disabled), you have to configure the proxy in the parameter fields below.
Proxy hostname or IP
| DB configuration name: | proxy_host |
The resolvable hostname or IP address of the proxy server.
Proxy port number
| DB configuration name: | proxy_port |
The port number the proxy server is listening on. Only numbers are allowed here, from range 1-65535. Any other values will lead to misfunctions. Often used values are "8080" or "3128".
Proxy username
| DB configuration name: | proxy_username |
If your proxy requires user authentification, enter a username here.
Proxy password
| DB configuration name: | proxy_password |
If your proxy requires user authentification, enter the valid password for the above defined user.
Proxy type
| DB configuration name: | proxy_type |
Different proxy types are supported, you should know which one fits your environment. Possible values are:
- SOCKS4
- SOCKS5
- HTTP
Use Seon proxy?
| DB configuration name: | seon_proxy_enabled |
If you want to use Seon proxy or Seon OFTP2 SmartProxy, enable this checkbox. Please refer to Seon Proxy and Seon OFTP2 SmartProxy for more detailled information.
ISDN parameters
Basic ISDN parameters for OFTP connections have to be defined here.
ISDN OFTP maximum buffersize
| DB configuration name: | oftp_default_buffersize_isdn |
As the TCP/IP maximum buffersize (as mentioned above), this numeric value reflects the maximum size of a OFTP data buffer. It may result to problems if this is set to values higher than your ISDN controllers can use for maximum transfer size, which is limited by CAPI2.0 to 4096 bytes. The minimum is 128 bytes. For configurations with problemous partners like old Seeburger products, please use 800 bytes as buffersize.
ISDN OFTP maximum credit count
| DB configuration name: | oftp_default_creditcount_isdn |
Same as the TCP/IP maximum credit count, this numeric value reflects the number of OFTP data exchange buffers before a little handshake will be done by the OFTP protocol. For configurations with problemous partners like old Seeburger products, please use 20 as credit count.
ISDN force confirmation of each DATA_B3 package
| DB configuration name: | isdn_force_confirm_each_data_b3 |
In ISDN, all data is transfered in 128 byte blocks, so-called "DATA B3 packages". Each package has to be confirmed by the remote partner, so the ISDN subsystem can remove unneeded memory and do some cleanup. If the remote partner doesn't confirm all DATA B3 packages, you may force him do so by enabling this checkbox. The ISDN subsystem sets a special flag in the DATA B3 package so nearly every ISDN counter system should confirm the receipt of that package, even if it's not explicitely implemented.
maximum amount of unconfirmed CAPI DATA B3 packages
| DB configuration name: | max_capi_sliding_window_size |
Different ISDN systems support a different amount of unconfirmed DATA B3 packages (see above). The normal CAPI standard of seven (7) unconfirmed DATA packages should never be reached, so you should be one or two packages lower than that limit in order to achieve the maximum of transport speed. Special CAPI ISDN implementations support more that the standard of seven packages, i.e. Bintec Bricks (they support up to 15). It doesn't make any sense to use that amount of unconfirmed data buffers, it doesn't speed up the transfer any more. If you receive CAPI timeouts, you should lower this amount of packages.
Don't wait for DATA B3 confirmation packages
| DB configuration name: | isdn_dont_wait_for_data_b3_conf |
If your ISDN system supports an extreme data throughput and nearly unlimited amount of unconfirmed DATA B3 packages lying around, you may ignore and don't wait for DATA B3 confirmation packages by enabling this highly unsupported feature. If you encounter line disconnects, disable this feature!
Background: In "normal" ISDN wildlife, each DATA B3 indication package indicates that other DATA B3 confirmation packages (up to this point of protocol transfer time) have been received. TIf you transfer very little files, it may be annoying waiting for each single data confirm package, you could send the file "as is" and wait for the OFTP protocol confirmation instead of waiting for the ISDN subsystem to acknowledge each single small piece of data sent. In some cases it's helpful, in most it's not! Just keep the setting disabled as long as you know exactly what you are doing!
enable CAPI keep-alive monitor
| DB configuration name: | capi_check_alive_monitor |
In order to use a Brick R4x00 or above, you have to enable this feature. Also, if you don't want to watch for Seon after a reboot of the Brick device, enable this feature. Activating this feature, Seon checks every defined controller every 60 seconds for availability. If a controller is inaccessible, it tries the connectivity again after 60 seconds. ---
Odette parameters
Default OFTP parameters for authentifications are configurable here. If no special columns are defined in the partner table below, these values will be used.
my default SSID, my default SFID, my default OFTP password, change every partner entry
| DB configuration name: | default_ssid, default_sfid & default_password |
These elements are only used for the web interface for creating new partners or for changing all partner values. If the checkbox is enabled, all partners in the partner table will get the new values for SSID, SFID and password on your side. If you don't configure columns in the partner table configuration below, these values are used for OFTP authentification.
Directories
In order to let Seon know where to find directories and files, these values have to be defined.
data incoming directory
| DB configuration name: | incoming_directory |
After successful file transfers (receiving), this directory defines where the incoming files will be stored. This directory must be on the same filesystem as the temporary directory (see below), otherwise you will get an error message in syslog (if enabled) that moving incoming files cannot be done. The filesystem must be dimensioned big enough to store a file with at most the maximum transfer size. I.e., if you receive a file of 200MB, you will need to have 200MB free on this filesystem, otherwise an error message will be sent to the partner (that the local filesystem is not big enough) and an entry to the receive log will be added.
data outgoing directory
| DB configuration name: | outgoing_directory |
This directory will be used by Seon Webaccess (which is part of Seon Enterprise) for outgoing jobs when initiating a send job. The plugins seonplugin_filemove and seonplugin_filecopy can refer to this directory by a configuration value.
temporary directory
| DB configuration name: | tmp_directory |
During incoming file transfers, the file fragments will be stored in this directory. Keep in mind (as mentioned above) to set this directory to the same filesystem as the incoming directory. The filesystem must be dimensioned big enough to store a file with at most the maximum transfer size. I.e., if you receive a file of 200MB, you will need to have 200MB free on this filesystem, otherwise an error message will be sent to the partner (that the local filesystem is not big enough) and an entry to the receive log will be added.
database backup directory
| DB configuration name: | backup_directory |
If you want to use the Seon backup mechanism, you need to define a directory where the SQL dump files will be stored. This directory is needed for the scripts "seonbackup" and "seonrestore".
binary installation directory
| DB configuration name: | bin_directory |
This directory points to your binary installation of Seon. It also contains the license key, so if you receive a license error, first check the existence of this directory and the file "license.key" in it. This entry is also used for the web interface to start the daemons.
script installation directory
| DB configuration name: | script_directory |
This directory points to your script installation of Seon. It contains helpful scripts, such as database backup and restore scripts and maybe other useful tools. The Seon web interface uses this definition.
absolute path to 'openssl'
| DB configuration name: | tcp_timeout |
DB configuration name: openssl_binary_path
Seon uses openSSL as basis for all OFTP 2 file security functions. The configured binary must exist and be executable for the user running Seon processes. The used openSSL binary must be of version 0.9.9dev, 1.0.0 or higher to fulfill the functionality for OFTP2.
absolute path to 'rrdtool'
| DB configuration name: | rrdtool_binary_path |
In order to use statistics, you have to define the path to „rrdtool“, the Round Robin database tool by Tobias Oetiker. The standard Seon distribution contains a pre-compiled version which works within Seon. If the file configured isn't executable, statistics are disabled. The program is used to create databases within Seon binaries, push data in it and to display the results as graphical output in the web interface. The latest version of "rrdtool" can be found under http://oss.oetiker.ch/rrdtool/. On his website he has also Amazon wishlists, so if you want to support his great work, please donate some gifts.
RRDB data path
| DB configuration name: | rrdb_datapath |
In this path, Seon creates, stores, modifies and searches the files for statistics. The directory must be writable by the user running Seon. If the path isn't writable or doesn't exists, statistics are disabled. For each partner, a file is generated for incoming transfer and for outgoing. The total consumption on the filessystem is about 315kB per partner.
absolute path to RRDtool TTF file
| DB configuration name: | rrdtool_font_path |
The statistical overview needs a font file (as Truetype font). Without this font file, you won't get any textual information in the statistic graphs.
SQL lost messages file
| DB configuration name: | sql_lost_messages_file |
If the configured MySQL server isn't reachable at any time, the SQL statements which are being sent to the MySQL server are logged into this file. If the file doesn't exists it will be created, so the directory must be writable for the user running Seon. The file itself (if it exists) must also be writable by the user running Seon.
Append datestamp to SQL lost messages file?
| DB configuration name: | sql_lost_messages_file_append_timestamp |
If enabled, in case of database inaccessibility, all SQL statements which could not be executed will be logged in the above configured "SQL lost message file", which gets a datestamp appendix to the filename. This datestamp consists of the following:
- a single dot ("
.") - year with 4 digits (like "
2009") - month with 2 digits (like "
03") - day with 2 digits (like "
27")
Example with a lost message fole configured to "/opt/seon/tmp/sql_lost_messages":
/opt/seon/tmp/sql_lost_messages.20090307
/opt/seon/tmp/sql_lost_messages.20090130
MySQL dump tool
| DB configuration name: | mysqldump |
As a useful tool from each MySQL distribution, the tool "mysqldump" is used in the Seon backup script for doing its job.
send test file
If configured correctly, Seon displays a link ![]() for test purposes for a partner. A given file can be sent with a given virtual filename to that partner for checking the OFTP connection.
for test purposes for a partner. A given file can be sent with a given virtual filename to that partner for checking the OFTP connection.
Events
First some words about the global behaviour of scripts:
event script usage
Every time the configuration of Seon is checked by a binary (which is at start time or when processing the signal 1 - SIGHUP), the event script configuration is checked. If a script is non-existant and/or the execute permissions don't allow the execution of a configured script, it won't get executed. No warning will be printed out or logged somewhere.
Presets exist (which are dynamically calculated with the last saved values for the scripts and binary directory configured here). These presets could be used for easy resetting the script configuration to either Seon Enterprise (Lite) and/or Seon 2 Core.
event script sleep time
Sometimes it is very handy if the event scripts are started with a little lag. This can be especially interesting if the „end receive“ or „end send“ scripts are called very fast because of small transfer files (i.e. ENGDAT abstract file). If you experience problems with your EDI system (i.e. it doesn't catch all files), try to increase the appropriate value. Keep in mind that the OFTP session waits that time you configured the sleep time. Setting the values very high increases the risk of a disconnect if the remote site has very little timeouts configured! More than 5 seconds should not be normal!
start send script
| DB configuration name: | start_send_script & sleep_start_send_script |
If a file is getting sent, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters.
end send script
| DB configuration name: | end_send_script & sleep_end_send_script |
If a file has finished (successfully or not) sending, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters.
xERP script
| DB configuration name: | xerp_script & sleep_xerp_script |
If an EERP or NERP (OFTP 2 only) message is received, this script will be started. Seon tries to find a send queue entry which conforms to the given parameters in order to set the values for comment, absolute path etc. If no send queue entry can be found that matches the given parameters in the EERP or NERP message, the script won't be executed. This script receives the same parameters as the end send script script.
start receive script
| DB configuration name: | start_receive_script & sleep_start_receive_script |
If a file is getting received, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters.
end receive script
| DB configuration name: | end_receive_script & sleep_end_receive_script |
If a file has finished (successfully or not) receiving, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters.
start session script
| DB configuration name: | start_session_script & sleep_start_session_script |
After a positive OFTP handshake, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters.
end session script
| DB configuration name: | end_session_script & sleep_end_session_script |
After a positive OFTP session, this script or program will be started with the documented parameters.
send queue entry blocked script
| DB configuration name: | blocked_script & sleep_blocked_script |
If a send queue entry gets blocked (i.e. wrong authentification, unsupported virtual filename at the remote site, connection problems), this scripts will be started. If more than one entry for a partner gets blocked, each send queue entry will start its own blocked script.
debug daemon log script
| DB configuration name: | seondebugd_log_script |
After a debug log has been written, this script will be started. This can be the case when asking for a debug log interactively (or with starting the appropriate program manually) or, if configured, when automatically created debug logs are written.
license script & trigger level
| DB configuration name: | license_script & license_script_hwm |
This script will be started after a configurable trigger level (in percent) is exceeded. Its main porpuse is to inform a responsible person that a new license should be obtained or other actions should be taken.
Enable automatic update mechanism & Seon automatic software update event
| DB configuration name: | run_updates_automatically & seonupdate_script |
If the value of run_updates_automatically is non-zero (if the checkbox is enabled), the automatic update script is started with the received file with the reserved virtual filename "SEON-UPDATE". This is normally a program of the Seon distribution in order to update the installation via signed files. This program changes its user context to the configured user (see: run Seon update program as user).
Seon automatic update post event
| DB configuration name: | configEventUpdatePost |
After a software update has been executed via the program "seonupdate", the configurable post event can be started, i.e. for cleanup reasons or informing system management hierachies.
enqueue post-script
| DB configuration name: | enqueue_post_script |
This script which will be executed after a successful enqueueing process.
Seon API proxy system log event script
| DB configuration name: | seonapi_proxy_systemlog_script |
This script which will be executed after a critical situation of the Seon Proxy will be logged in the Seon system log.
Daemon parameters
The behaviour of all binaries and Seon programs can be influenced here.
run Seon programs as user
| DB configuration name: | running_as_user |
When starting as user "root", all Seon binaries will try to switch to this configured user, if available on the running system. Subsequent calls of scripts and other programs are also done in the context of this user. This is extremely useful for runlevel scripts.
Double-check that this user exists in the system running Seon, that is has a home directory which is accessible and writable and that this user has a shell configured which is runnable!
run Seon update program as user
| DB configuration name: | running_update_as_user |
If enabled below, automatic software update are being run using this specific username. If changing to the context of this given user fails, the whole update procedure fails. If no username is configured, superuser "root" is used.
time slice for send queue daemon
| DB configuration name: | seonsqd_sleep_time |
The send queue daemon „seonsqd“ waits this amount of seconds before looking at the send queue table and react as needed (send one more entry, wait more time etc.).
time slice for receive daemon
| DB configuration name: | seonrd_sleep_time |
The receiving daemon „seonrd2“ waits this amount of seconds before looking at the configuration table and react as needed (wait more time or stop itself).
delete send queue entries
| DB configuration name: | delete_after_transfer |
This checkbox defines if the send queue table entries should be deleted (not the files itself, only the entry!) after a successful send. (If you need to delete the file itself, you should use the end send script, which gets the absolute filename as a parameter).
If this option is enabled, it automatically disabled the following option "Cleanup of sent send queue entries".
Cleanup of sent send queue entries
| DB configuration name: | configSendqueueCleanup |
If enabled, the send queue daemon cleans up the send queue for all entries with a given age automatically (based on the timestamp of "last change"). Optionally, an event "Send queue cleanup event" will be executed.
Age of send queue entries for cleanup (days)
| DB configuration name: | configSendqueueCleanupDays |
Send queue entries in status "successfully sent" with the last change date older than this amount of days will be taken into account for automatic cleanup.
Delete file, if available
| DB configuration name: | configSendqueueCleanupDeleteFile |
If this option is enabled, the automatic cleanup mechanism will delete the referenced file on the filesystem. If file deletion will take place, a log message will look like:
Deleted send queue entry '<virt. filename>' and file '<abs. filename>'
If this option is disabled or the referenced file doesn't exist, the log message says:
Deleted send queue entry '<virt. filename>'
let all files of send queue be fetchable
| DB configuration name: | fetch_all_from_remote |
Since polling is supported from remote systems, you can define files to be pollable. If you enable this checkbox, all files in your send queue which are in state of "new in queue" and "ready for remote fetch" will be sent in an OFTP session to the partner (otherwise, only entries "ready for remote fetch" are fetchable).
overwrite existing incoming files
| DB configuration name: | seonrd_overwrite |
If the incoming file exists in the "incoming directory", you can define to overwrite it. Otherwise, the partner will receive an error message saying that the local file already exists. (this might be useful for partners who don't like to reiceive an EEPR [end-to-end- response] message right after a successful filetransfer).
default maximum send tries for send queue daemon
| DB configuration name: | seonsqd_max_tries |
The send queue daemon "seonsqd2" will try to send one or all entries this amount of times. After this amount of unsuccessful tries, one or all send queue entries for that partner will be blocked (which will also get logged into the send log). All entries for a partner get blocked, if a connection problem occurs (i.e. invalid SSID/SFID or password, no physical connection to partner, wrong ISDN number or TCP/IP address etc.). One entry will be blocked if the partner doesn't accept this file. The other files are not affected by that error (i.e. wrong virtual filename, wrong alternative SFID of originator or destination).
additional sleeping time for send queue daemon & additional sleeping time factor for send queue daemon
| DB configuration name: | seonsqd_add_time & seonsqd_add_time_factor |
You can influence the time the send queue daemon „seonsqd2“ will sleep before it tries to send an send queue entry. The formula for calculating the additional sleep is as follows:
(add. waiting time) = (connect try)*(add. sleeping time)*(add. sleeping time factor)
progress bar refresh time
| DB configuration name: | progressbar_refresh |
Seon will update all file transfer progress information after this value (in seconds). Because it is database driven, some MySQL server will crash if you have too many connects to a database in a very short time (which could occur if you transfer very little files with a combination of a small exchange buffer size). If you experience problems with your database server, try increasing this value.
allow unsecure OFTP 2 authentification
| DB configuration name: | oftpv2_allow_unsecure_auth |
If an OFTP 2 partner is requested to use OFTP 2 authentification but he doesn't support this feature, you may allow to authentificate this partner with the OFTP 1 methods by enabling this checkbox. If you insist to use OFTP 2 authentification, disable the checkbox, so the partner will receive an error message that OFTP 2 secure authentification is needed.
delete temporary created files of OFTP 2 session
| DB configuration name: | oftpv2_delete_temp_created_files |
Seon creates temporary files by enqueueing files to the send queue or by directly sending a file to an OFTP 2 partner (if the partner is configured to use signing, compression and/or encryption). These temporary files can be deleted by Seon automatically, but you may also want to keep them for later archiving.
local character set
| DB configuration name: | oftpv2_original_charset |
OFTP 2 supports UTF-8 formatted information and error messages within the protocol and also extended virtual filenames (up to 999 bytes of UTF-8 formatted text). To translate the UTF-8 text into your local character set and to translate command line interaction from your local character set to UTF-8, you have to define your local character set here. If your local character set isn't listed here, you can define it in the database (table: "seon_configuration") manually by entering the character set descriptor in the line where „name“ is "oftpv2_original_charset". All character sets which are supported by "iconv" are supported by Seon. You get a list of supported character sets on the command line with the program:
iconv -l
if installed.
Unblock blocked send queue entries after successful connect?
| DB configuration name: | unblock_blocked_sendqueue_entries_after_poll |
If enabled, this options lets the Seon poll binary and receive daemon unblock blocked send queue entries after a incoming or outgoing connection to this partner has been successfully established.
Disable file restart functionality?
| DB configuration name: | configDaemonDisableFilerestart |
If enabled, Seon doesn't offer file restart functionality (which is offered by default if the communication partner supports it). In this case, the partner is told not to support file resuming, so aborted file transfers will restart in future sessions from the beginning of the file.
Disable automatic database cleanups / optimizations?
| DB configuration name: | configDaemonDisableMysqlOptimizeTables |
Seon cleans up database tables after a successful delete operation (in MySQL via "OPTIMIZE TABLE", in SQLite via "VACUUM" command). Enabling this configuration option disables the automatic cleanup of tables. Warning: could make your database grow in size if you don't clean up on your own!
enable OFTP message checker
| DB configuration name: | oftp_message_checker |
To secure your server, an OFTP message checker examines each transfered package for validity. This suppresses protocol attacks from remote and helps to avoid NULL pointer exceptions and other well-known attacks.
send queue entry status after abort
| DB configuration name: | sendq_entry_status_after_abort |
You can define the status of a send queue entry after manual abort here. It may be useful to avoid a race between an administrator and the send queue daemon if he aborts the file transfer but the send queue daemon grabs it afterwards because the time slice has taken account. Valid options are "new in queue", "successfully sent", "blocked" and "ready for remote fetch".
enable statistics & RRDtools refresh time
| DB configuration name: | enable_statistics & rrd_refresh |
As configured above with the RRDtool paths and directories, you have the possibility to activate or deactivate the scripting functionality here. The statistics contain the average transfer speed of a partner (incoming and outgoing as separate databases). If any of the above configured RRDtool path or binary is unavailable, scripting is disabled, even if you enable it here. The refresh time is the time is seconds when statistical data is transfered into the Round Robin database. This time period depends also on the database configuration of the RRDB and is closely dependant from the creation process which is intergrated into Seon (if an RRDB file doesn't exist). The default of 10 seconds should not be changed!
NEW: If statistics are enabled, a seperate logging table will be filled with information how many files have been transfered (in the ways "sent" and "received" with or without success. This amount of transfered filed is being displayed in the partner list and the partner "edit" details.
Append timestamp to received file
| DB configuration name: | rec_append_timestamp_to_filename |
Some partners may send you files with the same virtual filename, but different timestamps. In order to receive these files properly, an appendix is added to the filename containing the announced timestamp of the file. This also helps to receive the same file from different partners at the same time. Beware: the timestamp syntax has changed from OFTP 1 to OFTP 2!
The appendix of the filename is as follows:
- OFTP 1.0 - OFTP 1.3: "
<datestamp><timestamp>0000", i.e. "200903171423590000" - OFTP 1.4 and OFTP2: "
<datestamp><timestamp><counter>", i.e. "200903171423590523"
The main difference between both names is that the "counter" field in older OFTP sessions will be emulated via "0000".
Append destination SFID to received file
| DB configuration name: | configDaemonAppendSFIDRec |
If enabled, the received file will contain the destination SFID attached with a dot (".") in front of the SFID to the filename. This influences both the temporary and absolute filename after transfer.
Append PID of receive process to received file
| DB configuration name: | configDaemonAppendPIDRec |
If enabled, the received file will contain the process ID (so-called "PID") attached with a dot (".") in front of the PID to the filename. This influences both the temporary and absolute filename after transfer.
OFTPv1: Don't wait for EERP message
| DB configuration name: | oftpv1_dont_wait_for_eerp |
The normal behaviour of a send queue item is as follows:
- new in queue: waiting for transfer
- taken by send queue: session active, waiting for transfer
- send in progress: active transfer
- waiting for remote acknowledge: waiting for EERP or NERP from partner
- successfully sent: partner acknowleged file (entry may be deleted if configured)
If an partner doesn't send an EERP message, the send queue entry will exist forever. In order to avoid this, the send queue entry may get the status „successfully sent“ after successful send by enabling this checkbox (and may be deleted if the above checkbox „delete send queue entries“ is enabled). Beware: the xERP scripts won't be executed any more because no send queue entry will be found matching the parameters given in any EERP or NERP message. This feature just affects OFTP v1 partners, not OFTP 2!
Enable automatic update mechanism?
| DB configuration name: | run_updates_automatically |
Activating this feature enables the usage of automatic software and lowers the administrative tasks to keep the software up-to-date.
Send queue daemon partner organizing mechanism
| DB configuration name: | sqd_partner_organizing |
If you want to configure a massive parallel installation to be handled by the send queue daemon without shared memory segments for information handling which partner has how many lines online, you may want to switch this configuration value to "database values". The default of "shared memory segments" works perfectly for single instances of Seon and should be set only this way. CAVEAT: when using database values only for parallel channel information on send queue partners, there exists a timeframe when the information is invalid (this is when the send queue daemon forks a new process up to the database update command execution). During this little amount of time, more parallel processes may exist than configured for this partner.
take ALL server IDs into account
| DB configuration name: | sqd_db_partner_organizing_all |
If the above configuration of "Send queue daemon partner organizing mechanism" is set to "database values", then only this server ID could be inspected or ALL used servers can be inspected for parallel channels. Enabling this checkbox is the recommended value for this configuration!
also take receive queue into account
| DB configuration name: | sqd_partner_organizing_use_recq |
If the above configuration of "Send queue daemon partner organizing mechanism" is set to "database values", it's possible to active the check of the send queue for active partner connections. This amount of active connections will be added to the calculation of active connections for opening new connections during send queue daemon handling.
Should Seon send queue daemon unblock all blocked entries on startup?
| DB configuration name: | seonsqd_unblock_on_start |
The default behaviour of Seon send queue daemon on startup: if enabled, the daemon unblocks all blocked send queue entry for the configured server ID. The behaviour up to 2007-11-24 was like enabling this feature.
Enable offline handling of OFTP2 transfered files?
| DB configuration name: | offline_oftp2_filehandling |
Since version 2007-12-01, Seon is able to handle OFTP 2 offline, so the security features of OFTP2 can be used in an insecure network segment. Enable this feature in order to use seon_oftp2_offlinehandling to handle the received files semi-manually.
pre-script for offline tool
| DB configuration name: | offline_oftp2_pre_script |
This script is executed before the handling process starts. It may be used to transfer the file itself from one location to another. Parameters are documented here
post-script for offline tool
| DB configuration name: | offline_oftp2_post_script |
This script is executed after the handling process starts. It may be used to clean up the environment. Parameters are documented here
remove successfully handled offline OFTP2 file entries
| DB configuration name: | oftp2_offlinefile_remove_entries |
If this flag is enabled, successfully handled files will be removed from the list of received files. It's highly recommended to turn this flag on.
Identify remote partner via incoming medium, too?
| DB configuration name: | partner_search_medium |
When enabled, the Seon receive daemon checks for the given medium the partner connects to the server and identifies the partner with this information in addition to the given SSID and password. This feature is very handy when several partner entries with the same SSID and password exist for different reasons.
Don't send EERP messages immediately in OFTP 1.x sessions?
| DB configuration name: | no_instant_eerp |
When enabled, Seon doesn't send instantly EERP (end-to-end-response) messages to the remote partner containing the default parameters. If enabled, you have to create the EERP message manually (or programatically) in order to be sent correctly to the partner.
Receive all files if partner is authentificated?
| DB configuration name: | receive_catch_all |
In order to receive ALL files of a authenticated partner (via SSID and password), without any check of locally defined originator and/or destination SFID, please active this checkbox. All files are being received without any error, even if no partner has been configured for this configuration of SFIDs. You should design your post-processing of the received file via the "end receive script" on your own.
Cleanup queues on daemon startup?
| DB configuration name: | cleanup_queues |
If enabled, a successful start of a send or receive queue daemons cleans up the respective queue with the following rules:
- server ID matches the started daemon
- send queue daemon "
seonsqd": Reset all files in status "taken by send queue" and "send in progress" to "new in queue" - receive queue daemon "
seonrd": Remove all files with the same server ID
Because it's a quite destructive option, the default is off.
Should invalid restart positions deactivate restart of file?
| DB configuration name: | dont_restart_invalid_offset |
If enabled, all files given with a restart position bigger than proposed file size won't restart file transfer and begin at the start of the file (i.e. if file size is 44123kB, but restart position is available at 49876kB, because the physical file is 51832kB big; received file size is bigger that the proposed 44123kB because the file is bigger).
Note: Volvo needs this flag to be turned on in special conditions.
Activate OFTP2 secure authentification directly after certificate delivery?
| DB configuration name: | activate_ssidauth_after_delivery |
If enabled, the partner switch "use OFTP2 secure authentification" will be enabled right after an automatic import of a certificate delivery. Please note that this may influence the behaviour of new connections: they may be aborted if the configuration flag allow unsecure OFTP 2 authentification is disabled and this partner wants to connect the next time and doesn't have the same settings activated.
Enable per-partner virtual file naming recognition?
| DB configuration name: | per_partner_sfiddsn |
If enabled, an incoming file will be checked against a list of configured partner entries with the configured SFID (originator and destination) and in addition to this normal behaviour, against a list of configured virtual filenames (so-called "DSN", "Virtual File Dataset Name" or "SFIDDSN"). These allowed virtual filenames are configurable at a per-partner basis, so they are an additional switch which partner entry is handling this special filename.
If multiple partner entries match, first one will be used.
Fetch EERPs?
| DB configuration name: | configDaemonFetchEerp |
If enabled, Seon's send queue daemon will contact the remote partner for every file which is in the send queue status "waiting for remote acknowledge". In the newly created session, the partner has the chance to send the EERP or NERP message for any file. The maximum amount of configured sessions for a partner is being used (if available and configured properly in the "partner table" configuration). No more than the maximum of this amount of sessions will be opened, summarized for poll queue, send queue files and EERP fetching entries.
Fetch EERPs every x timeslice
| DB configuration name: | configDaemonFetchEerpTimeslice |
If EERP fetching is enabled, this factor is being used to increase the time between two connect tries of the Seon send queue daemon when trying to fetch one or more EERP messages of a partner.
Fetch EERPs for ISDN partners, too?
| DB configuration name: | configDaemonFetchEerpIsdnToo |
Since 2016-11-28, by default Seon only fetches EERPs for TCP/IP and TLS partners (before this release, also ISDN partners are being contacted for missing EERPs). If you activate this checkbox, also ISDN partners are being contacted for missing EERPs (files in the send queue with status "waiting for remote acknowledge). Be aware that in combination with the send queue daemon time slice parameter and the EERP timeslice factor, the send queue daemons initiates outgoing sessions which can generate connection costs!
Don't deactivate dir.scanner entries on error?
| DB configuration name: | configDaemonDirscannerDontDeactivate |
If enabled, the send queue daemon will not deactivate diresctory scanner entries if an error occurs with the according enttry (i.e directory not available, permission errors etc.). By default, this configuration option is disabled and the daemon will deactivate such entries, logging this in the system logs.
Allow underscore character ("_") in virtual filenames?
| DB configuration name: | configDaemonAllowUnderscoresInVirtFilenames |
Some OFTP and OFTP2 systems out in the wild support the underscore character in virtual filenames, which is unsupported by the RFC. In order to support this common mistake of standard interpretation, Seon supports this non-standard character in addition to the well-defined characters, which are:
The numerals: 0 to 9 The upper case letters: A to Z The following special set: / - . & ( ) space
Seon Enterprise
The behaviour of Seon Enterprise can be influenced in the following three topics:
Seon Enterprise - Basic
is Seon Enterprise installed?
| DB configuration name: | seon_enterprise |
If you enable this checkbox, the web interface expands its funtionality needed to administrate Seon Enterprise, an enhanced version of Seon. Disabling this checkbox turns Seon into its default configuration of Seon Core. If you are interested in features of Seon Enterprise, contact your software dealer or write an email to info@seon.de .
default country
| DB configuration name: | default_country_idx |
When creating a new company entry in the Seon partner database and using Seon Enterprise, a country has to be selected for this partner. For easy administration, a default country is configurable with with configuration. This configuration is only visible if Seon Enterprise is installed (and the above checkbox is enabled).
default receive plugin group
| DB configuration name: | default_rec_plugin_pkg |
This pulldownmenu contains all defined plugin packages. You should select a plugin package which will be run after a job is completely received (i.e. after the receive file sorter has collected all needed files). This configuration is only visible if Seon Enterprise is installed (and the above checkbox is enabled).
default send plugin group
| DB configuration name: | default_send_plugin_pkg |
The configured default send plugin group is used to pre-configure a plugin group which is used for newly added partners. This plugin group will be configured at company level (the highest hierarchy level) for the new partner.
enable multi-protocol support?
| DB configuration name: | seon_enterprise_other_protocols |
In order to enable other protocols in addition to OFTP and OFTP2 (which is handled via the Seon send queue for outgoing files), you may define and use other protocols for data transfer to partners. Enable this checkbox to get more options on then. See Seon Enterprise - other protocols for more details about administration.
define own company
| DB configuration name: | seon_enterprise_own_company |
For a finer grained target address code search, you can define your own company here. If "no selection - enable multi-client-support" is selected, all address codes of all companies will be used for recipient search.
Default recipient for incoming jobs
| DB configuration name: | enterprise_default_rec |
By default, no recipient is configured for inomcings jobs in initial state. By defining a default recipient here, this person will be defined as the initial recipient, leading to an execution of the configured plugin group of this recipient if no other plugin changes this recipient successfully.
Path for jobs of directory scanner
| DB configuration name: | enterprise_dirscanner_jobdir |
This name defines the path (relative to the outgoing directory) wherein the directory scanner will create jobs. The job number will be appended to this given directory name. Relative path information can be used, too (using "../" definitions).
Examples (with a default outgoing directory path of "/opt/seon/outgoing"):
- definition:
seon-dirscanner-enterprise-job- - resulting path (for job 123):
/opt/seon/outgoing/seon-dirscanner-enterprise-job-123/
Enable auto-addresscode functionality
| DB configuration name: | enterprise_auto_adrcode |
When enabled, editing a recipient adds the ability to create a new unique address code, based on values of other persons in that company. The algorithm tries to identify a numeric element of the existing address code and increments it until an unused value is available. This functionality may fail for address codes without a numeric element.
Enable addresscode uniqueness checks
| DB configuration name: | enterprise_unique_adrcode |
When enabled, the administrative web interface warns an administrator if the configured address code is used by another person in the same company. This is done by marking the input field as invalid, adding a hover mask for a textual information that this address code is used already.
Disable automatic addresscode conversion
| DB configuration name: | configGuiAddresscodeDontConvert |
When enabled, the administrative web interface doesn't convert the addresscode into upper case, so it's usable for other purposes than ENGDAT routing.
Shall errornous sendings abort jobs
| DB configuration name: | configEnterpriseAbortJobRejectedFiles |
When enabled, the "end send" event of Seon Core will abort jobs if sending is errornous.
Absolute AJAX URL for job restore processes
| DB configuration name: | enterprise_archive_restore_url |
For archived jobs, this URL will be called via JSONP in order to restore the job.
Name of parameter for restore AJAX call
| DB configuration name: | enterprise_archive_restore_parametername |
When restoring Seon Enterprise jobs via the above configured URL, this is the name of the parameter containing the archive ID.
Event to be executed for sent non-Enterprise files
| DB configuration name: | non_enterprise_send_event |
If you use Seon Core and Seon Enterprise events in parallel, this event will be fired if a "end_send" will be executed for non-Enterprise enqueued files.
Name of JSONP callback parameter
| DB configuration name: | enterprise_archive_restore_callbackname |
Due to JSONP, this is the name of the required callback function parameter. The default value (if empty) is "callback".
Seon Enterprise - Webaccess
Webaccess login logo URL
| DB configuration name: | webaccess_login_logo |
An alternative logo URL (absolute or relative is supported) for displaying in the login prompt of Seon Webaccess.
Webaccess logged in logo URL
| DB configuration name: | webaccess_loggedin_logo |
When defined, a customized logo can be added to the logged-in view of Seon Webaccess in the top right corner. Absolute or relative URLs are supported.
Encrypt Webaccess session information
| DB configuration name: | webaccess_session_encrypt |
If required, Seon Webaccess can encrypt the session information in the database via AES256 algorithm and hashed via SHA1 hashing algorithm.
Compress Webaccess session information
| DB configuration name: | webaccess_session_compress |
If required, Seon Webaccess can compress the session information in the database via bzip2 algorithm.
Don't show receive queue view
| DB configuration name: | webaccess_disable_recq |
If you don't want the receive queue to be displayed to end-users in Seon Webaccess, enable this checkbox. The receive queue view doesn't contain any administrative operations.
Don't show send queue view
| DB configuration name: | webaccess_disable_sendq |
If you don't want the send queue to be displayed to end-users in Seon Webaccess, enable this checkbox. The send queue view doesn't contain any administrative operations.
Show incoming jobs without recipient
| DB configuration name: | webaccess_show_invalid_rec_jobs |
When enabled, this feature adds jobs without a valid recipient to the list of incoming jobs for all users.
Session timeout (min)
| DB configuration name: | webaccess_session_timeout |
You can set a session for timeout for Seon Webaccess sessions here. Without any interaction, an old session expires automatically after that amount of minutes.
Highlight address code in ENGDAT filenames
| DB configuration name: | webaccess_highlight_addresscode |
If ENGDAT filenames are not interpreted into real filenames (as given i.e. in ENGDAT abstract files, these files are quite technical to read. In order to highlight the address code contained in the filename, enabling this configuration options offers to highlight this address code with the following methods:
- bold (configuration variable "
webaccess_highlight_addresscode_bold") - underlined (configuration variable "
webaccess_highlight_addresscode_underline") - italic (configuration variable "
webaccess_highlight_addresscode_italic")
Show all incoming jobs of department
| DB configuration name: | webaccess_show_dep_jobs_incoming |
Seon Webaccess normally shows only jobs of the corresponding user who is logged in. In order to show all incoming jobs of the department the user is contained, enable this checkbox.
Show all outgoing jobs of department
| DB configuration name: | webaccess_show_dep_jobs_outgoing |
Seon Webaccess normally shows only jobs of the corresponding user who is logged in. In order to show all outgoing jobs of the department the user is contained, enable this checkbox.
Include given name in search
| DB configuration name: | webaccess_search_given_name |
When searching for persons in Seon Webaccess (in any situation), the given name (aka. the "first name") is not searched for by default. By enabling this configuration option, searching for the given name is being activated, too.
Don't show popup when adding recipient
| DB configuration name: | webaccess_ignore_recipient_add |
When adding a new recipient to a send job, a popup occurs when not enabled. If enabled, no popup will occur.
Seon Enterprise - Plugins
The default behaviour of all plugins can be changed here. The behaviour can be overridden by a configured, set up at each level of partner hierarchy.
OFTP2
OFTP2 relevant options are configurable here:
delete temporary created files of OFTP 2 session
| DB configuration name: | oftpv2_delete_temp_created_files |
If enabled (all other values than zero, '0') all files created for temporary usage in OFTP2 sessions and session preparations will not be deleted. This is useful for debugging the created files and meta-information.
Enable offline handling of OFTP2 transfered files?
| DB configuration name: | offline_oftp2_filehandling |
If enabled (all other values than zero, '0') incoming OFTP2 files (which need to be handled by any security mechanism, such as signature checking, decompression and/or decryption, will be held in an offline queue, which will then be evaluated by the Seon offline daemon.
pre-script for offline tool
| DB configuration name: | offline_oftp2_pre_script |
If OFTP2 offline handling is enabled, you may enter here the absolute path to an executable which will be executed by the Seon offline handler before the offline handler processes the file. This is normally a transferer script.
post-script for offline tool
| DB configuration name: | offline_oftp2_post_script |
If OFTP2 offline handling is enabled, you may enter here the absolute path to an executable which will be executed by the Seon offline handler after the offline handler has processed a file. This is normally a cleanup script.
remove successfully handled offline OFTP2 file entries
| DB configuration name: | oftp2_offlinefile_remove_entries |
If OFTP2 offline handling is enabled, successfully processed files will be removed from the offline queue (the database table only, not from the filesystem!) if this feature is activated.
Activate OFTP2 secure authentification directly after certificate delivery?
| DB configuration name: | activate_ssidauth_after_delivery |
If enabled, Seon activates secure authentification method for the given partner right after an automatic certificate exchange.
Don't send EERP messages immediately in OFTP2 sessions?
| DB configuration name: | no_instant_oftp2_eerp |
After successful receipt of an OFTP2 file, you may suppress the automatic sending of an EERP by activating this feature. You should ensure to send an EERP via "seoneq" with all parameters given in the "end receive script".
Send EERP in synchronous session?
| DB configuration name: | configOftp2SyncEerp |
In OFTP2, file handling (like decompression, signature verification and decryption) is being processed in an asynchronous, forked process (because this handling can take a very long time in terms of network connections; many minutes are not uncommon). If you have to deal with synchronous data transfers where an EERP MUST be transfered in the same OFTP2 session, you can enable this option. Beware of the (default: 1MB) size limit of received files for enabling this feature.
Maximum size of sync. EERP files (in kB)
| DB configuration name: | configOftp2SyncEerpMaxsize |
If the above mentioned synchronous EERP handling for OFTP2 is enabled, you have to define a filesize limit of the transfered file. Files bigger that this limit are not handled by the synchronous EERP process.
Add log entry for synchronous EERP handling
| DB configuration name: | configOftp2SyncEerpLog |
If synchronous file handling takes place, an optional log entry can be places in the receive log every time this process is activated. Warning: may increase your receive log massively!
Delete original OFTP2 handled files which have been enqueued by send queue daemon?
| DB configuration name: | deleteToBeEnqueuedTouchedFiles |
If a file, which has been in status 10 ("to be enqueued for OFTP2"), may result in a temporary OFTP2 file if one of the options for OFTP2 file handling is enabled (compression, signing or encryption). If this is the case, the original file would stay in it's original state. When enabling this feature, Seon deletes this original file for security reasons from the filesystem. WARNING: no undo or recovery is available!
OFTP2 security policy
Starting with Seon release 2016-08-16, you can define which security settings match your internal company security policy with easy-to-answer configurations. The following parameters help to configure these values in an easy way. These settings are only relevant for the reception of files, sending files with another settings is possible nevertheless with potentionally different partner settings.
The following configuration options can be defined to a behaviour explained below:
- File encryption (dabase configuration name: "
oftp2_policy_encrypted") - File compression (dabase configuration name: "
oftp2_policy_compressed") - File signature (dabase configuration name: "
oftp2_policy_signed")
The configuration options explained:
- unconfigured: All files are accepted
- Allow: All files are accepted, both with activated and deactivated security option.
- Require: The security option MUST be activated for incoming files, otherwise the file will be rejected with an appropriate error message.
- Reject: The security option MUST NOT be activated for incoming files, otherwise the file will be rejected with an appropriate error message.
- Require partner value: Require partner value: The file must be sent by the remote party according to the settings which are activated or deactivated in your partner configuration. If the security option is not fulfilled, the file will be rejected with an appropriate error message.
If a security policy is not fulfilled, an offered file will be rejected. A log entry in the receive log will occur per file. The partner is given the information not to retry this sending process again.
Allow fallback to unsecure OFTP 2 authentification
| DB configuration name: | oftpv2_allow_unsecure_auth |
If enabled (all other values than zero, '0') it is possible to connect to Seon with a disabled secure authentification mechanism, even if the identified partner (via SSID and password) has a secure authentification method activated. If this configuration is disabled (which is the default), OFTP2 sessions are directly closed with a secure session error message.
Preferred cipher suite
| DB configuration name: | oftp2_policy_preferred_cs |
This configured cipher suite will be the preferred one for incoming files. With the option below, files using another cipher suite can be rejected. The list of cipher suites is dynamically obtained from the OFTP2 system. If the configuration value is "Use partner configured value", incoming files shall (or must, depending on the option below) be using the cipher suite which is defined at partner level.
Deny other cipher suites than the preferred
| DB configuration name: | oftp2_policy_deny_unpreferred_cs |
If a ciphersuite is configured in "Preferred cipher suite" and incoming files use another cipher suite, this option will reject the incoming file with an appropriate error message.
External IP address or hostname of this OFTP2 system
| DB configuration name: | oftp2_external_hostname |
This configuration option is used in new certificate signing requests as the common name ("CN") of this OFTP2 system.
Activate auto-cleanup of old certificates?
| DB configuration name: | configOftp2AutoCleanup |
Since certificates will expire, Seon will warn you about this fact. If you want Seon to clean up expired certificates automatically (so you don't have to do this manually), you can enable this checkbox.
Automatically enable disabled certificates?
| DB configuration name: | configOftp2AutoEnableInactiveCert |
If an old certificate has been archived by the mechanism above, disabled (say: not yet enabled) certificates can be enabled dynamically. This is also a mechanism for automatic handling during certificate renewal.
Logging
Logging enables Seon to insert human readable messages into log tables. You may turn some features on or off to suite your needs.
use syslog
| DB configuration name: | use_syslog |
If you turn on this checkbox, major errors will be logged to the server's syslog facility with the severity LOG_ERR. Major errors are table misconfigurations or process dependant messages (fork failures, memory allocation problems etc.).
enable log vault
| DB configuration name: | enable_log_vault |
Enabling this feature activates code to move log entries from the direct access log tables to slower log vault tables, where all messages (older than a configurable amount of days) are kept. This enhances the access to the online logs.
maximum age for fast logs
| DB configuration name: | logvault_days |
After this amount of days, log entries will be moved from one log to the vault.
move send logs every x timeslices
| DB configuration name: | logvault_sendq_timeslices |
The entries older than the above configured value ('maximum age') of the send log will be moved to the slower vault every this amount of time slices of the send queue daemon. This configuration value cooperates with the configuration value 'time slice for send queue daemon'. Only logs belonging to that server ID will be moved to the vault!
move receive logs every x timeslices
| DB configuration name: | logvault_recq_timeslices |
The entries older than the above configured value ('maximum age') of the receive log will be moved to the slower vault every this amount of time slices of the receive queue daemon. This configuration value cooperates with the configuration value 'time slice for receive daemon'. Only logs belonging to that server ID will be moved to the vault!
archive received xERP messages & archive sent xERP messages
| DB configuration name: | oftpv2_archive_received_xerp & oftpv2_archive_sent_xerp |
It may be useful archive positive and/or negative end-to-end responses. These xERP messages can be seen as acknowledgements from the partner (received xERP) or from yourself (sent xERP). The web interface contains a archive viewer on the left hand: "xERP log". This feature may be needed in some countries for legal issues.
enable script logging
| DB configuration name: | enable_script_logging |
Enabling this feature logs all script calls, parameters, returncodes and output to the script logs. In the web interface, you can take a look at the script logs with the link „Script log“. In this interface, you can also restart event scripts (even if they have changed in the configuration: you can then execute the original or the new one, depending on executability of the script file).
Enable directory scanner logging?
| DB configuration name: | enable_dirscanner_logging |
If enabled, the directory scanner logs every single execution script based on the found file.
Enable continuous write of Seon debug daemon output?
| DB configuration name: | seondebugd_continuous_write |
When enabling this feature, the Seon debug daemon creates a debug log file (and starts the configured event script if existant) after the ring buffer is full. In this case, no message is lost.
If this feature is enabled, starting with Seon release 2015-08-25 a button with the label "Collect today's logs" is available which lets you send all collected debug daemon dump files of this day and enqueue it to a specific partner for debugging. Requirements for this feature are:
- Seon debug daemon is running
- The temporary directory is accessible and writable by the Seon debug daemon
- The event "debug daemon log event" does not change the filename prefix "seon-logfile-<YYYYmmdd>" (where "YYYY" is the current year with four digits, "mm" is the actual month starting at "01" with two digits and "dd" is the actual day, starting with "01" and two digits).
The partner to which the files are being enqueued is possible to be searched. By default, the partner "Seon-Update" is searched. If the partner is not found, no partner search is pre-set and the whole partner list is being presented. If exactly this pre-set partner "Seon-Update" is found, it it selected automatically, so you don't have to click on it to activate the selection. Only if a single partner is selected in the partner search list, the files are being enqueued to this partner after submission (either via "Save" button or via double click).
The virtual filenames of the logfiles is "Seon-LOGFILE-<counter>" where "<counter" is an incremented number, starting with 1 (one). The comment of the automatically enqueued files is "Seon logs - automatically enqueued via administrative web interface".
Absolute path to logfile of Seon API
| DB configuration name: | seonapi_logfile |
The Seon API, which is the background service for Seon Webaccess and Seon Proxy, logs into this file.
Seon API loglevel
| DB configuration name: | seonapi_loglevel |
The above configured file will be written in the configured log level.
Suppress unsuccessful connect log entries?
| DB configuration name: | suppress_unsuccessful_connect_logs |
If an incoming connection fails before OFTP handshake could be initiated, a logging entry is normally made in the style of:
unsuccessful connect try from IP 'aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd'
If you want to ignore these messages (i.e. when using a system monitoring which just watches if the TCP/IP port is open), enable this feature.
GUI
The GUI offers some parameters which influence the default behaviour.
Send signals to running processes
| DB configuration name: | webgui_kill_processes |
The PHP backend can send running processes a signal, i.e. for reloading their configuration (when clicking "Save") or cancelling transfer processes. If the webserver is not running on the same machine as the Seon daemons do, or if the webserver user is not privileged to send signals to running Seon processes (i.e. they are running in another user context), you should disable this checkbox, otherwise (which is the default) keep it activated for a seamless integration of GUI and backend.
Disable PID check of daemons
| DB configuration name: | disable_PID_checks |
The Seonapi can check if daemons which should run with a given process ID really exist. If they don't exist, the Seonapi will cleanup running information (= their PIDs) in the database. This feature is available in Linux and MacOS, partially in AIX. If you get unwanted results, disable this feature.
Show partners with unknown medium
| DB configuration name: | display_partners_with_unknown_medium |
Since the configurable partner database schema is highly configurable, many partner entries may have an unknown transmission medium configured (valid values are configurable for ISDN, unencrypted TCP/IP and encrypted TCP/IP aka. TLS). If this configuration option is enabled, all partners (even with unknown medium values) are displayed in the partner list.
Enable simple configuration
| DB configuration name: | simple_config_gui |
In many installations, most complex situation are not needed for this installation. As a minimizer for unneeded configuration options, most uncommon configuration options are not visible when enabling this configuration option. Elements which are hidden when this config option is activated are:
- Configuration:
- TCP/IP
- ISDN
- Events
- Daemon
- OFTP2
- Logging
- Partner table
- Programs:
- Partner import
- Cipher suites
Partner management for OFTP2 is also more easy, so a more or less incomplex system will be shown in order to allow non-common users to administrate the system well.
Min. age for expiration warning of certificates
| DB configuration name: | gui_cert_warning_days |
The administrative web interface can show expiring certificate warnings and expired certificate errors in the tab "Welcome", section "Possible configuration problems". The configured amount of days are used for calculation which certificates to display.
Theme for administrative GUI
| DB configuration name: | gui_theme |
The admin web interface supports the switch of the used theme for displaying information. You can switch the theme without saving dynamically. When saving this config, all subsequent calls to the web interface will switch to the configured theme.
Disable health check of database
| DB configuration name: | gui_disable_db_healthcheck |
Disabling the database health check will not include database table checks in the section "Possible configuration option" in the "Welcome" tab of the administrative web interface. By disabling these checks, you can lower your database overhead massively.
Filtered filesystems from "Welcome" tab
The administrative web interface shows the filling state of all mounted filesystems, except the filesystems contained in the list of excluded filesystems. A filesystem can be exluded from the displayed list by clicking on the entry bar on the "Welcome" page, then answering "Yes" to the delete question. The deleted file system(s) are listed here in a grid, where they can be removed so the removed entry will be displayed again on the welcome page.
User own defined URLs
| DB configuration name: | use_own_defined_urls |
If enabled, the menu on the left side in the administrative web interface will add an entry with a configured name (see below).
Name of entry
| DB configuration name: | own_defined_urls_menuentry_name |
The name of the menu entry which contains user-defined URLs is changeable.
Own defined URLs
If enabled, the administrative web interface adds the possibility to configure a list of URLs for viewing within the administrative web interface as a closeable tabbed entry. The included URL is being integrated via an IFRAME, so if the integrated page doesn't allow this functionality (i.e. thorugh a META tag), the content will stay empty. Keep in mind that many popular dynamic sites don't allow this type of integration. Have a look into your JavaScript console if any errors occur.
Send queue displayed columns
The list of columns configure the default state of the columns when opening the send queue overview. The columns can be re-activated afterwards via the column header management.
other interesting configurable values
Some values are not configurable via web interface, but also have a useful meaning when running Seon. These configuration value names are:
seonclientd_port: TCP/IP port of the program Seon client daemonwebinterface_path: Absolute path of the web interface on the webserver. This is useful for upgrading processes in order to update the path correctly.