Seon create log dumps
Contents
What are Seon dumps?
Seon log dumps are binary files containing deep information about the system, like SQL statements, their results, network traffic, OFTP status information etc. Every Seon program generates Seon log messages, which are organized by the daemon "seondebugd" (Seon debug daemon).
Requirements
In order to get an Seon debug dump file, the daemon must be running. Verify this by checking the daemon's running state. The daemon must be running at least for three seconds in order to gather all needed information.
Normal behaviour
All Seon programs send their log information to the Seon debug daemon. The daemon uses a ring buffer to save the logged messages, so with a limited amount of entries, the daemon will overwrite old entries when the buffer is full. The daemon process size depends on the amount of entries saved in memory. The more entries are configured, the bigger the process grows. A normal state should be about 2-5 MB in memory.
Generating a dump
When a critical situation occurs, the daemon should be initialized to dump its content to an Seon debug dump file. This can be in two ways:
- via web GUI
- via command line
Dumping log via web GUI
1. Select "Programs" -> "Daemons" in the administrative web interface:
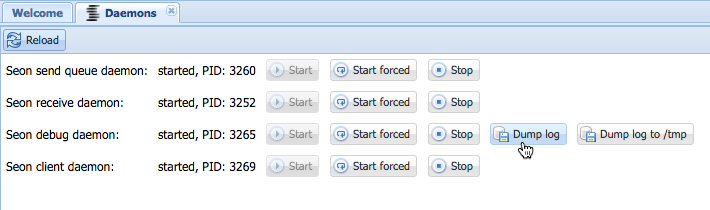
2.1 In the new panel, click on the button "Dump log", which is activated when the daemon is running:
If the daemon is not running, it makes no sense to start it and dump for an ancient event: the event must occur when the daemon "seondebugd" is running.
2.2 If the previous step fails, it may help to dump a log to the directory "/tmp", since the Seon's configurable temporary directory may be not available. Use the button "Dump to /tmp" in order to accomplish this task.